- 1 What is a TFT LCD Display Module?
- 2 Key Components of a TFT LCD Module
- 3 Types of TFT LCD Display Modules
- 4 Standard TFT LCD
- 5 IPS TFT (In-Plane Switching)
- 6 High Brightness TFT
- 7 Bar-Type and Custom Aspect Ratios
- 8 Round or Circular Displays
- 9 Transflective and Reflective TFT
- 10 Why the Right Module Matters
- 11 Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a TFT LCD Display Module
- 12 Display Size and Active Area
- 13 Resolution and Pixel Density
- 14 Brightness and Contrast Ratio
- 15 Viewing Angle Technology
- 16 Interface Types
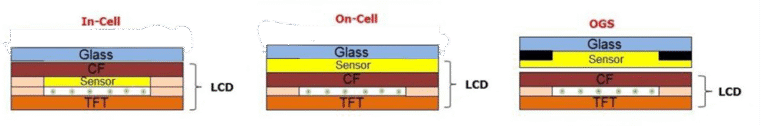
- 17 Touch Panel Support
- 18 Operating Temperature Range
- 19 Backlight Lifetime
- 20 Power Consumption
- 21 How to Match a TFT LCD Display Module to Your Application
- 22 Industrial Equipment & Automation Panels
- 23 Medical Devices and Diagnostics
- 24 Automotive Dashboards and HMIs
- 25 Wearables and Compact Consumer Devices
- 26 Outdoor or Battery-Powered Products
- 27 Mechanical Integration and Customization
- 28 Evaluating TFT LCD Display Module Suppliers
- 29 Key Evaluation Criteria
- 30 Technical Documentation
- 31 Sample Availability & Lead Time
- 32 Communication & Support
- 33 QA and Traceability
- 34 Cost Optimization Without Cutting Corners
- 35 Practical Cost-Saving Strategies
- 36 Long-Term Cost Considerations
- 37 System Integration: Software & Driver Support
- 38 Platform Compatibility
- 39 Display Drivers and Libraries
- 40 Tuning Touch Sensitivity
- 41 Final Thoughts: Build Smarter with the Right Display Module
- 42 FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- 43 Reference Resources
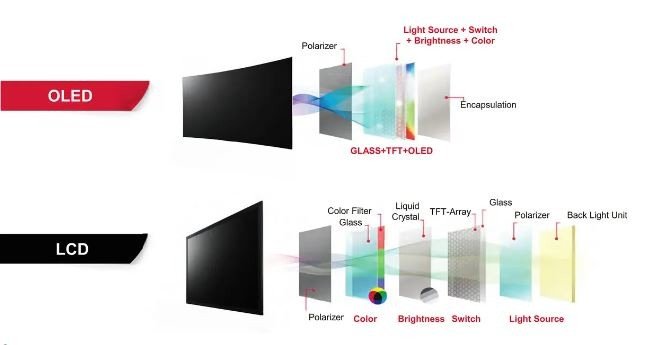
What is a TFT LCD Display Module?
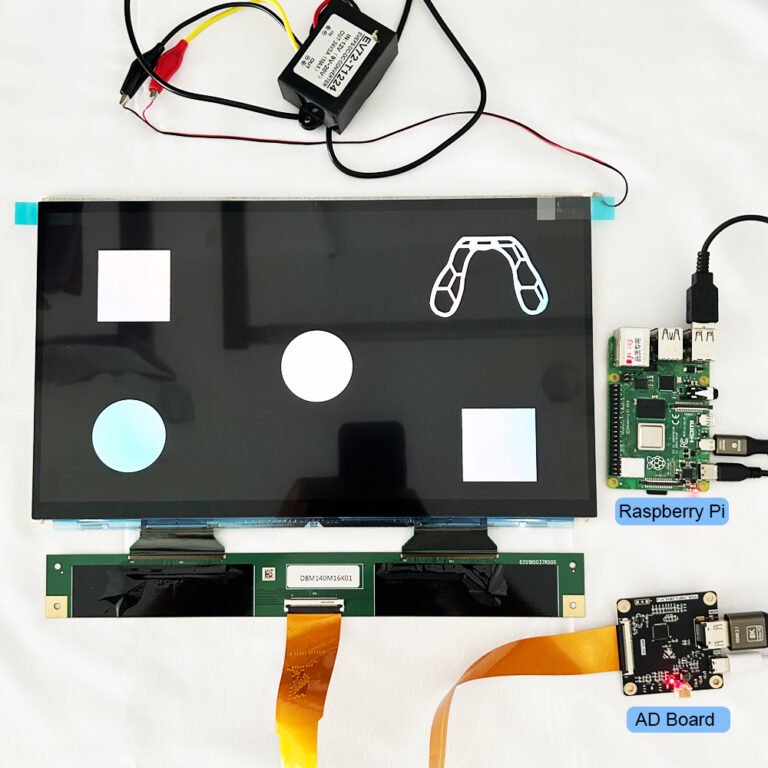
A TFT LCD display module is a self-contained unit that includes a thin-film transistor (TFT) LCD panel, a backlight, driving electronics, and sometimes touch capability. It serves as a human-machine interface (HMI) in a variety of devices such as medical monitors, control panels, automotive dashboards, and smart appliances.
While the term “TFT LCD” refers to the display technology itself, the “module” includes all supporting components required to drive and display content, making it a plug-and-play solution for engineers and developers.
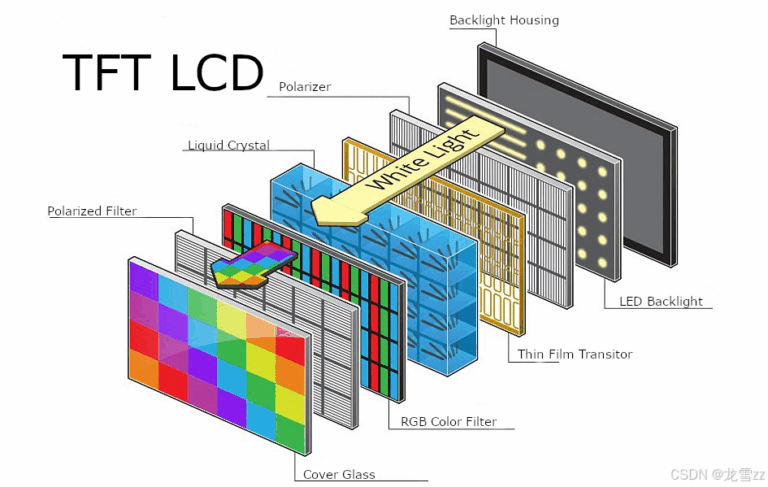
Key Components of a TFT LCD Module
- TFT Panel: The main display surface where pixel data is rendered.
- Hintergrundbeleuchtung: LED-based system providing illumination, usually white LEDs.
- Treiber-IC: The chip that receives image data from the host processor and controls pixel updates.
- FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit): Cable connecting the display to the mainboard, often customizable.
- Touch Panel (optional): Resistive or capacitive sensors for user interaction.
- Cover Lens or Housing (optional): Offers protection or mechanical integration.
Each component can be tailored depending on the needs of your specific application.
👉 Verwandte Lektüre: What is LCD : Define LCD Display
Types of TFT LCD Display Modules
TFT LCD modules come in a wide variety of configurations, and choosing the wrong type for your application could lead to performance issues or over-engineering. Understanding the categories can help you narrow your selection:
Standard TFT LCD
The most common type. Affordable, readily available, and used in general consumer or industrial products where advanced visuals are not a priority.
IPS TFT (In-Plane Switching)
Provides better color accuracy and wider viewing angles. Ideal for devices where color fidelity and readability from all directions are important, such as medical equipment and automotive displays.
High Brightness TFT
Optimized for sunlight readability, with brightness levels over 800 nits. Suitable for outdoor kiosks, e-bikes, agriculture machinery, or industrial HMIs exposed to ambient light.
Bar-Type and Custom Aspect Ratios
Modules with non-standard shapes like 3:1, 5:2, or 1:1. Used in automotive dashboards, shelf labels, or any custom UI layout.
Round or Circular Displays
Mostly used in smartwatches, fitness trackers, or instrument clusters. They require special PCB and driver configurations to match the circular form.
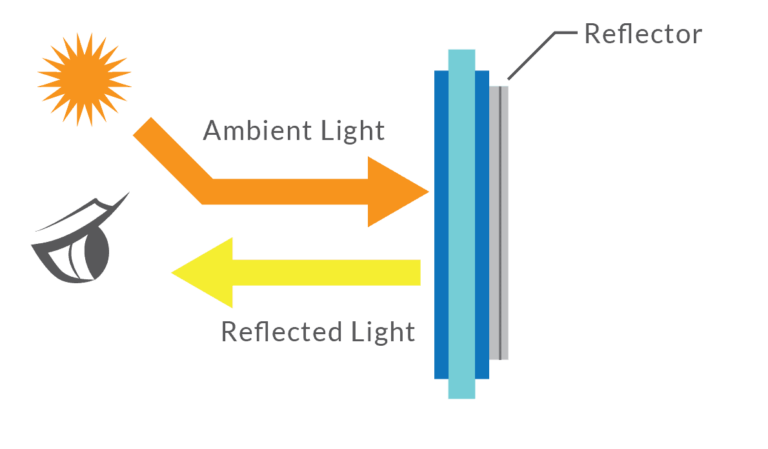
Transflective and Reflective TFT
Ideal for ultra-low power or outdoor applications. These panels leverage ambient light instead of or in addition to backlight, reducing power draw.

Why the Right Module Matters
Choosing a display module isn’t just a checkbox in your BOM. It has direct implications on:
- User Experience: A display with poor brightness or limited angles could lead to frustration.
- System Integration: Wrong interface type or resolution can mean extra work or incompatibility.
- Power Efficiency: Crucial for portable or solar-powered systems.
- Product Durability: Industrial and automotive devices need high reliability across temperature and usage conditions.
- Development Timeline: Custom FPCs or drivers not matching your embedded platform can delay deployment.
A well-chosen tft lcd display module ensures your product performs reliably, stays within budget, and meets user expectations.
Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a TFT LCD Display Module
Choosing the right TFT LCD display module isn’t just about screen size—it’s about identifying the right combination of performance, efficiency, and durability for your specific application. This section breaks down the critical specs you must evaluate when selecting a module, whether you’re building a handheld device, a rugged control panel, or a wearable product.
Display Size and Active Area
One of the first specifications to consider is the diagonal screen size, typically ranging from 0.96″ to over 10″. More important than just the size, however, is the active area—the portion of the screen where content is actually displayed.
- Small modules (<3.5″): Ideal for wearables, handheld tools, or small interface devices.
- Medium modules (4″–7″): Common for smart appliances, medical monitors, and industrial controllers.
- Large modules (>7″): Used in infotainment, point-of-sale terminals, and vehicle dashboards.
Tip: Always check that the housing and UI design aligns with both the module’s outer dimension and active display area.
Resolution and Pixel Density
Resolution determines how sharp your images, text, and UI elements will appear. It’s expressed as width × height in pixels, e.g., 480×272, 800×480, oder 1280×720.
- Higher resolution = more detail, but also more GPU load and power usage.
- Lower resolution = reduced detail, but often sufficient for simple interfaces.
Pixel density (PPI – pixels per inch) matters most in close-range devices like smartwatches, while dashboards or kiosks may get away with lower PPI.
Recommendation: Match resolution with expected UI complexity. If you’re displaying text and vector icons only, QVGA (320×240) might be enough. For rich images, at least 720p is recommended.

👉 Verwandte Lektüre: What is the difference in LCD resolution?
Brightness and Contrast Ratio
Brightness is measured in nits (cd/m²). For indoor applications, 250–400 nits is standard. For outdoor or semi-outdoor use, look for:
- 600–800 nits for good visibility in daylight
- 1000+ nits for direct sunlight readability
Contrast ratio, defined as the ratio between the brightest white and the darkest black the screen can produce, influences readability and visual quality. IPS panels often provide better contrast ratios than TN panels.
Tip: Be sure to factor in the viewing environment when selecting brightness specs.
Viewing Angle Technology
Die Betrachtungswinkel determines how clearly the screen can be seen when viewed from different directions. Technologies vary:
- TN (Verdrehte Nematik): Narrow angles, lower cost
- IPS (In-Plane-Switching): Wide angles (up to 178°), best for user-facing applications
- VA (Vertikale Ausrichtung): Great contrast, moderate angles
- All O’clock or Wide Viewing: Indicates the screen is viewable from all directions
Use case example: An e-bike display needs wide-angle readability from above, below, and side angles—IPS or All O’Clock is ideal.

👉 Verwandte Lektüre: Der Betrachtungswinkel von TFT-LCD-Bildschirmen
Schnittstellen-Typen
The interface determines how the display communicates with your main processor. Common interface types include:
- SPI / QSPI: Simple, used in MCUs and low-speed applications
- MCU (8/16-bit parallel): Fast, straightforward for many embedded platforms
- RGB Parallel: High-speed data transfer, used in mid-performance systems
- MIPI-DSI: High-speed, low-power differential signaling for high-resolution displays
- LVDS / eDP / HDMI: Common in large, high-end or plug-and-play displays
Developer note: Always check whether the display driver IC is compatible with your platform (e.g., STM32, NXP, Rockchip, etc.).
Touchpanel-Unterstützung
Many TFT LCD display modules come with touch panel integration—either as a standard feature or optional.
- Kapazitive Berührung (PCAP): Supports multi-touch, fast response, high transparency. Ideal for consumer and medical use.
- Resistive Berührung: Operates via pressure. Glove- or stylus-friendly. Best for industrial environments.
Touch performance depends on factors like touch IC, firmware tuning, and surface treatment. Some modules allow custom firmware calibration to optimize glove or water touch performance.
👉 Verwandte Lektüre: Was sind die Unterschiede zwischen TN, VA und IPS?
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial or outdoor applications demand modules with extended temperature ranges:
- Standard Range: 0°C to +50°C (for indoor consumer products)
- Wide Range: –20°C to +70°C or even –30°C to +85°C (for automotive or field use)
Exceeding the rated range can cause image persistence, slow response, or permanent damage.
Backlight Lifetime
The lifespan of the backlight (usually LEDs) is crucial for long-term applications. Most industrial modules offer:
- Typical lifetime: ≥20,000 hours
- High-end modules: Up to 50,000 hours
Some modules include PWM dimming control oder ambient light sensors to extend backlight life by reducing brightness intelligently.
Stromverbrauch
Power efficiency is critical for battery-powered devices. Key contributors include:
- Backlight brightness and efficiency
- Interface speed (e.g., MIPI vs. SPI)
- Refresh rate and frame buffer usage
Tip: For solar or portable use cases, consider reflective or transflective TFT modules with low power idle states.
How to Match a TFT LCD Display Module to Your Application
Every application has its own set of technical and user demands. Understanding these will help you align your TFT LCD display module’s specifications to real-world usage. This section breaks down the most common use-case categories and recommends suitable module types for each.
👉 Check out our extensive industry applications
Industrial Equipment & Automation Panels
Key Considerations:
- Wide temperature range (–20°C to +70°C)
- Durable front glass or touch panel
- Glove-friendly operation (resistive touch or industrial PCAP)
- High brightness for factory lighting
- Long-term supply chain stability
Recommended Specs:
- IPS panel with 400–800 nits brightness
- Resistive or industrial capacitive touch
- MCU or RGB interface for embedded systems
- Anti-glare coating and 50,000-hour backlight life
Medical Devices and Diagnostics
Key Considerations:
- Precise color rendering for accurate imaging
- Anti-fingerprint or anti-microbial coating
- Capacitive multi-touch for intuitive interaction
- High contrast and resolution
Recommended Specs:
- IPS panel with at least 720p resolution
- PCAP with firmware tunable to gloves or styluses
- Brightness: 400–600 nits
- EMI-certified modules (e.g., CE/FCC)

Automotive Dashboards and HMIs
Key Considerations:
- Wide operating temperatures (–30°C to +85°C)
- High contrast and brightness for sunlight readability
- Circular or ultrawide formats for gauge integration
- Quick wake-up and refresh rates
- Glove compatibility, rugged construction
Recommended Specs:
- High-brightness IPS or transflective TFT
- Round or bar-type modules
- Capacitive touch with automotive-certified IC
- MIPI-DSI or LVDS interface
Wearables and Compact Consumer Devices
Key Considerations:
- Compact size (1.2″–2.8″)
- Low power consumption
- Lightweight design
- Stylish round or square shapes
- Multi-touch support
Recommended Specs:
- AMOLED or IPS TFT with capacitive touch
- Brightness: 300–500 nits
- SPI or MIPI interface
- Optical bonding and curved surface support
Outdoor or Battery-Powered Products
Key Considerations:
- Lesbarkeit bei Sonnenlicht
- Energy efficiency
- Long backlight life
- Wide temperature range
Recommended Specs:
- Transflective or high-brightness TFT (≥800 nits)
- Reflective LCD for ultra-low power devices
- LED backlight with PWM control
- Optional frontlight for nighttime readability

Mechanical Integration and Customization
When integrating a TFT LCD module into your product, consider:
- Mounting holes or brackets
- FPC direction and length
- Bezel opening and alignment
- Cover lens options (glass thickness, silk printing, logos)
- Touch and display alignment precision
Manufacturers often offer low-MOQ customization services. You can specify:
- Brightness level
- Interface position or connector type
- Frame or housing compatibility
- Anti-reflective or anti-glare coatings
Evaluating TFT LCD Display Module Suppliers
Finding the right TFT LCD display module is only half the equation—the other half lies in choosing a reliable manufacturer or supplier. A technically sound module can still fail if it comes from a partner lacking in quality control, support, or supply stability.
Key Evaluation Criteria
Technical Documentation
A trustworthy vendor will provide:
- Detailed datasheets (mechanical, optical, electrical specs)
- 2D/3D drawings for design integration
- Reference circuit diagrams
- Display timing charts and initialization code
- Touch panel I²C or SPI protocols
Red Flag: Vendors who hesitate to share documentation or only provide minimal specs.
Sample Availability & Lead Time
Check how quickly they can:
- Ship samples for evaluation (typically <7 days)
- Begin pilot production runs
- Scale to mass production volumes
Suppliers with in-stock modules or semi-custom SKUs shorten your go-to-market timeline.
Communication & Support
Look for:
- Direct engineer support (not just salespeople)
- Ability to provide display tuning (touch sensitivity, brightness)
- Experience working with your application sector
If your team needs help with integration, a display supplier that speaks your platform’s “language” is a game changer.
QA and Traceability
A professional supplier will:
- Label each display with serial numbers
- Maintain batch tracking for defect analysis
- Provide burn-in or aging test data
- Offer failure analysis support
Certifications such as ISO9001 and RoHS compliance should be verifiable and current.
Cost Optimization Without Cutting Corners
Reducing the cost of a TFT LCD display module doesn’t mean compromising quality—it means making smart trade-offs that don’t affect critical performance.
Practical Cost-Saving Strategies
- Standard Resolution: Stick to popular formats (e.g., 320×240, 800×480) to benefit from mass production economies.
- Simplified Touch: Choose resistive touch for cost-sensitive industrial devices.
- Lower Brightness (Indoor Use): If used indoors, you may not need 1000+ nits brightness.
- Integrated Touch + Display: One bonded unit saves assembly cost and thickness.
- FPC or Backlight Customization: Reduce component waste by tailoring only what you need.
- Avoid Unnecessary Coatings: Anti-glare or AR coatings add cost—only include them when visibility is affected.
Long-Term Cost Considerations
- Backlight Lifetime: Longer LED life reduces service/replacement costs.
- Vendor Stability: Sudden EOL (End of Life) can force expensive redesigns.
- Ease of Assembly: Pre-bonded or plug-and-play modules save time on the production line.
System Integration: Software & Driver Support
Your display may be perfect on paper—but it needs to work smoothly with your system’s hardware and software.
Platform Compatibility
Ensure your module:
- Has the correct signal voltage (1.8V, 3.3V, etc.)
- Matches the timing requirements of your processor
- Supports initialization via provided driver code (especially for SPI/MIPI)
Common platforms include:
- STM32, NXP i.MX, Rockchip, TI, Raspberry Pi
- Embedded Android/Linux SBCs
- Custom RTOS microcontrollers

👉 Related reading: What are the differences between TN, VA, and IPS?
Display Drivers and Libraries
Ask your supplier for:
- C or C++ display drivers
- Framebuffer support (Linux)
- Touchscreen calibration tools
- Sample GUI integrations (LVGL, TouchGFX, Qt)
This minimizes integration work and debugging during development.
Tuning Touch Sensitivity
For capacitive touch:
- Get access to tuning tools for ICs like FT5x06, GT911, or ILITEK
- Adjust sensitivity for glove, water, or stylus input
- Prevent “ghost touches” or edge dead zones
Bonus Tip: Bonded modules (LCD + touch panel + cover glass) reduce ghosting and dust ingress, improving overall reliability.
Final Thoughts: Build Smarter with the Right Display Module
Choosing a TFT LCD display module isn’t about finding the most advanced screen on the market—it’s about finding the right screen for your product.
With thousands of variations available, your best approach is a strategic one: define your application needs, prioritize key specs, and partner with a supplier who can provide the technical support, quality assurance, and customization flexibility your product deserves.
From resolution and brightness to touch integration and cost control, every decision counts toward building a better device—and a better experience for your end user.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between TFT and IPS?
TFT is the underlying technology, while IPS is a type of TFT panel with better color accuracy and viewing angles.
Can I use a TFT LCD display outdoors?
Yes, with a brightness of at least 800 nits and optional anti-glare or transflective technology.
What’s the lifespan of a typical LCD module?
Most offer LED backlight lifespans of 20,000–50,000 hours under standard conditions.
How do I choose between SPI and MIPI interfaces?
SPI is ideal for simple, low-resolution modules. MIPI supports high-speed data and is better for high-resolution or video-rich displays.
Are custom FPC layouts possible?
Yes. Many manufacturers offer FPC length, shape, and pinout customization—even at low MOQ levels.
Do TFT modules support multi-touch?
Yes, capacitive touch modules support gestures and up to 10 points of contact depending on the IC and firmware.
Referenz-Ressourcen
- MIPI Alliance. (2021). Display Serial Interface (DSI) Specification. Retrieved from https://www.mipi.org/specifications/display-interface
- STMicroelectronics. (2023). TouchGFX Framework for Embedded Displays. Retrieved from https://www.st.com/en/embedded-software/touchgfx.html
- NXP Semiconductors. (2023). i.MX Applications Processors Graphics User’s Guide. Retrieved from https://www.nxp.com
- Raspberry Pi Foundation. (2023). Display Configuration Guide. Retrieved from https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/display.html
- LVGL Developers. (2024). LVGL – Light and Versatile Graphics Library. Retrieved from https://lvgl.io
- Digi-Key Electronics. (2024). TFT Display Modules Product Selector Guide. Retrieved from https://www.digikey.com/en/products/display-modules
- Mouser Electronics. (2024). LCD Display Modules Selector. Retrieved from https://www.mouser.com/c/optoelectronics/display-modules/lcd-modules/
- Panelook. (2024). Worldwide LCD Display Panel Database. Retrieved from https://www.panelook.com/
- International Organization for Standardization. (2011). ISO 9241-303:2011 Ergonomics of human-system interaction – Electronic visual displays. Geneva: ISO. Retrieved from https://www.iso.org/standard/50909.html
- European Commission. (2023). RoHS Compliance Guidelines – Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive. Retrieved from https://ec.europa.eu/environment/topics/waste-and-recycling/rohs-directive_en
- UL Solutions. (2023). UL Display Reliability and Environmental Test Standards. Retrieved from https://www.ul.com/
- Goodix Technology. (2023). Capacitive Touch Tuning Tools and Firmware. Retrieved from https://www.goodix.com/en/products/touch/hmi