- 1 Why Lamination Matters: Real-World Value You’ll Notice
- 2 Understanding the Layers: From LCD to Finished Glass Stack
- 3 Types of Lamination: OCA, LOCA, or Leaving an Air Gap
- 4 Dry Lamination – OCA Film
- 5 Wet Lamination – LOCA / OCR Resin
- 6 Air Gap (No Lamination)
- 7 Lamination Process Unpacked: A Step-by-Step Flow
- 8 Benefits That Engineers Actually Appreciate
- 9 Enhanced Optical Performance
- 10 Better Touch Accuracy
- 11 Increased Mechanical Strength
- 12 Reduce Fogging Risk
- 13 Technical Considerations & Trade-offs
- 14 Which Adhesive to Use?
- 15 Bubble Management
- 16 Alignment Precision
- 17 Rework & Repair
- 18 Trends & New Frontiers
- 19 Common Problems & Pitfalls
- 20 Real Use Cases: Lamination in Action
- 21 FAQs
Why Lamination Matters: Real-World Value You’ll Notice
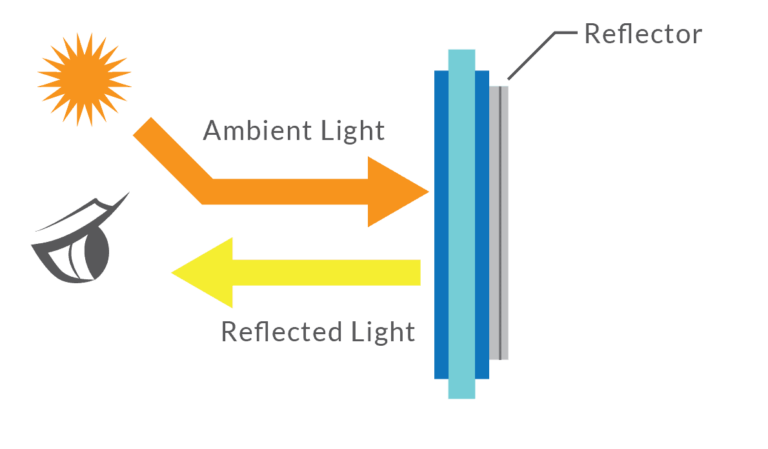
When you bond the cover glass, touch panel, and LCD into a solid, gap-free stack, something magical happens. You stop losing contrast to internal reflections. Your display becomes more dust- and moisture-resistant. The screen survives knocks that would crack unbonded glass. And your touch responsiveness improves—especially in rugged or outdoor settings.
Optical bonding, one of the most common lamination approaches, has been shown to reduce internal reflections by up to 65%, improving contrast and readability in bright conditions—all without boosting backlight power. It even prevents condensation between layers (goodbye fog!) by sealing out moisture completely.
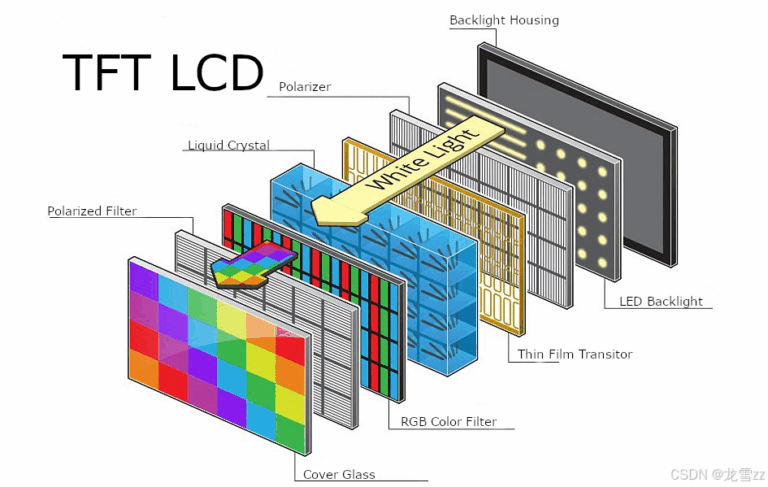
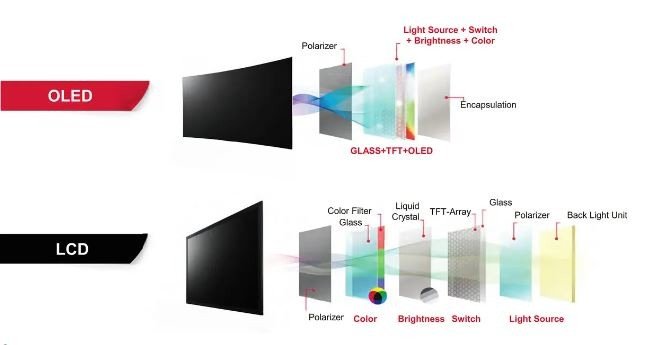
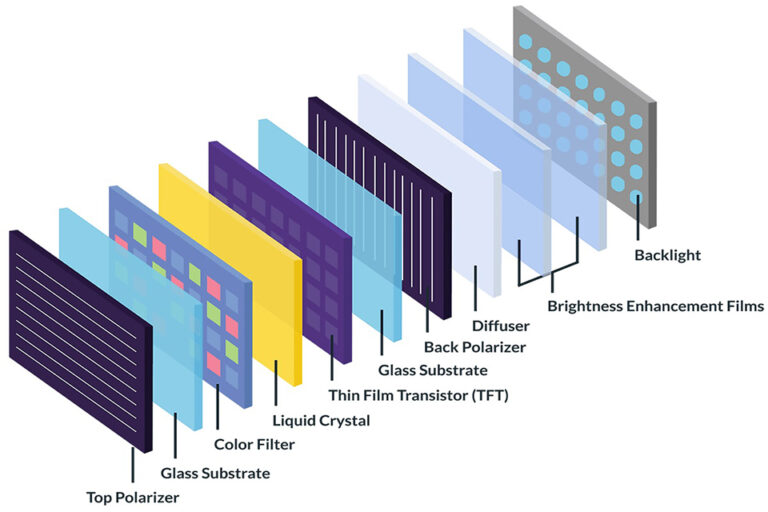
Understanding the Layers: From LCD to Finished Glass Stack
A laminated TFT LCD stack typically includes:
- Cover glass or lens
- Optional touch sensor layer (e.g. PCAP)
- Optically clear adhesive (OCA or LOCA)
- Painel LCD TFT
Every micron of alignment matters. Misaligned adhesives or uneven pressure can introduce visible optical distortions or touch inaccuracies.
Types of Lamination: OCA, LOCA, or Leaving an Air Gap
Dry Lamination – OCA Film
Pre-cut adhesive film is placed between the glass and display, then bonded under heat and pressure. It’s quick, repeatable, and well-suited for high-volume production—though it struggles to compensate for slight irregularities in surfaces
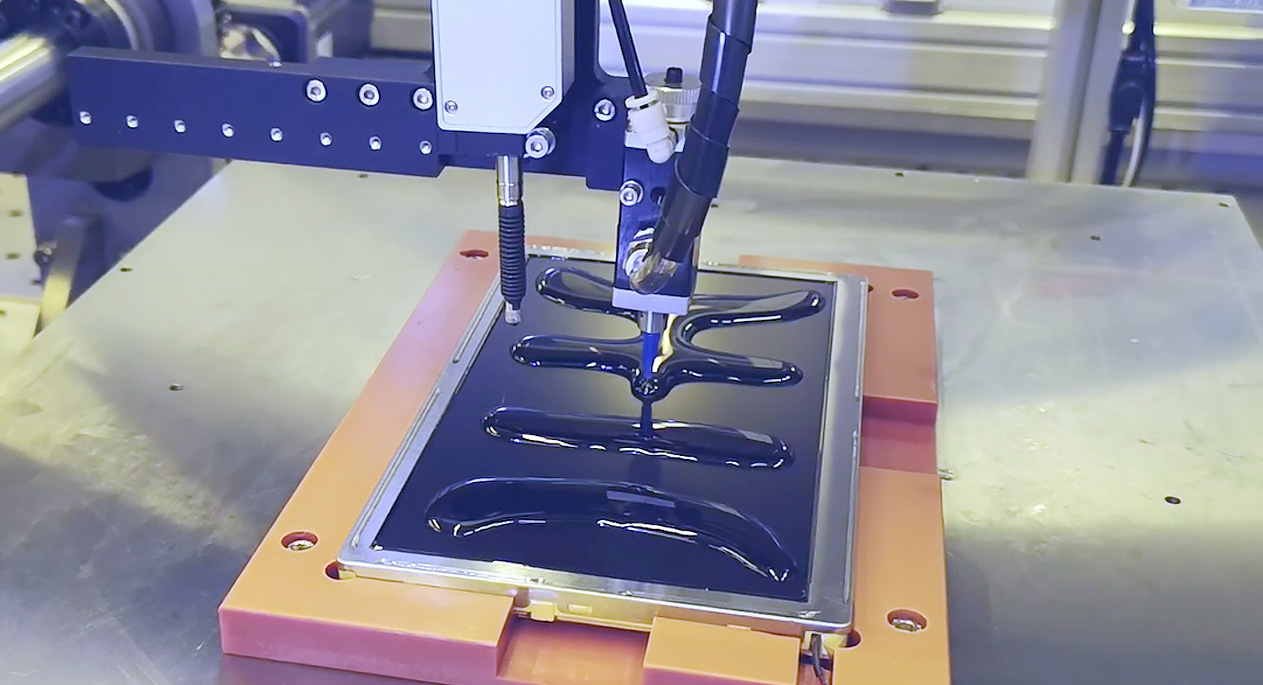
Wet Lamination – LOCA / OCR Resin
Liquid adhesive is dispensed precisely, flows to fill gaps, and then cures (often via UV). This allows air-bubble-free bonding with complex glass shapes and touch components. LOCA offers better gap tolerance and reworkability, though it requires clean, controlled operation. Early sources on mobile repair forums warn about messy LOCA handling and emphasize that it’s increasingly deprecated in favor of OCA due to long-term consistency issues.
Air Gap (No Lamination)
Simple spacer-based approach—fast, cheap, and easy to rework. But it allows internal reflection, reduces touch clarity and durability, and is not appropriate for harsh environments.
Lamination Process Unpacked: A Step-by-Step Flow
- Cleaning & Pre-Alignment: Glass and panel are bathed in cleaning solution, then aligned by robotic or visual systems in cleanroom settings.
- Adhesive Application: OCA film is placed and bonded; LOCA is dispensed via syringe or dosing equipment.
- Bonding & Compression: Layers are compressed evenly under vacuum or heat to eliminate air and secure adhesion.
- Curing: Films use heat or pressure; LOCA typically cures under UV light.
- Quality Check: Inspect for bubbles, misalignment, adhesion strength, stray moisture or touch anomalies.
These steps require tight control: even one speck of dust can ruin optical clarity. Hence Class‑1000 (ISO 6) or better environments are common in manufacturing.
Benefits That Engineers Actually Appreciate
Enhanced Optical Performance
With no air gap, ambient light doesn’t bounce around between layers. Result: brighter images, stronger contrast, and readability even under direct sunlight—without increasing backlight intensity.
Better Touch Accuracy
Removing parallax (the visual shift when touching through a gap) enables more accurate, immediate touch response. Perfect for medical or industrial touch UIs.
Increased Mechanical Strength
The bonded adhesive layer absorbs shock and prevents dust or moisture ingress. It’s a structural reinforcement, not just cosmetic protection.
Reduce Fogging Risk
Condensation between air layers is eliminated. That solves a common long-term reliability issue in humid, temperature-variable environments.
Technical Considerations & Trade-offs
Which Adhesive to Use?
- OCA film: Fast, low-waste, consistent—but struggles with uneven surfaces.
- LOCA/OCR resin: Flexible and gap-filling—but UV curing and handling must be precise to avoid defects.
Quality LOCA avoids yellowing (commonly seen in epoxy or polyurethane adhesives), lasting longer in high UV or temperature conditions.
Bubble Management
Liquid adhesives like LOCA present a risk of bubble formation if curing is uneven or contaminants enter. Even one bubble can create visible artifacts or weak touch sensitivity.
Alignment Precision
Even a 10 µm offset or tilt can cause visual distortion or skewed touch. High-precision alignment rigs and vacuum bonding tools are critical in production.
Rework & Repair
Removing bonded layers (especially LOCA) is difficult. OCA removals are slightly easier but still risky. Most surfaces are considered permanent after bonding.
Trends & New Frontiers
- Flexible and curved displays increasingly use LOCA-style resin that can tolerate bending while maintaining clarity.
- Nano-textured and anti-reflective coatings now combine with lamination for glare reduction without sacrificing color fidelity.
- UV-resistant, flexible silicone adhesives extend display lifetimes and reduce shrink-related issues common in acrylic-based bonding systems.
Common Problems & Pitfalls
- Delamination often stems from surface contamination or misalignment during bonding.
- Yellowing may appear with low-grade adhesive over time, especially in UV-rich environments.
- Touch drift or ghosting can occur when bubbles or uneven glue placement compromises sensor responsiveness.
- Repairs: bonded modules often cannot be disassembled without damage—best to get it right first time.
Real Use Cases: Lamination in Action
- Automotive displays employ LOCA bonding for anti-vibration strength and sunlight-readability.
- Industrial HMIs rely on sealed bonding to resist dust, moisture, and condensation in harsh factory settings.
- Medical monitors use high-grade bonding for sharp visuals, consistent touch, and hygienic sealing.
- Digital signage & kiosks benefit from glare reduction and vandal resistance via bonding.
FAQs
What’s the difference between OCA and LOCA lamination?
OCA is a solid adhesive film—fast, clean, consistent; LOCA is liquid resin—fills uneven surfaces, offers better slope tolerance but requires careful curing.
Is lamination always necessary?
Not always. For indoor, low-cost screens with no touch or sunlight exposure, air gap methods can suffice. But bonding significantly enhances performance for most rugged or interactive applications.
Do laminated screens hold up outdoors?
Absolutely—with anti-reflective coating and proper adhesive selection, laminated displays perform far better in sunlight and temperature extremes than unbonded counterparts.
Does lamination improve touch accuracy?
Yes—bonding eliminates parallax, bringing the touch sensor closer to the user and improving responsiveness.
Does lamination make displays more expensive?
It does add manufacturing cost, but the trade-off in usability, reliability, and visual quality usually offsets the extra expense.