- 1 Understanding the Basics: What is OLED Display?
- 2 How Does OLED Display Technology Work?
- 3 Types of OLED Displays
- 4 OLED vs LCD: The Core Differences
- 5 Advantages of OLED Displays
- 6 Limitations of OLED Displays
- 7 Applications of OLED Displays
- 8 Why OLED Displays Are the Future
- 9 Should You Choose an OLED Display?
- 10 Conclusion
Understanding the Basics: What is OLED Display?
Um OLED display is a type of flat-panel display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current passes through them. Unlike LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays), which rely on a backlight to illuminate pixels, OLED displays are self-emissive. This means each pixel generates its own light and can be turned on or off independently.
The result is true black levels, infinite contrast ratios, and vibrant color reproduction, making OLED one of the most visually impressive display technologies available today.
How Does OLED Display Technology Work?
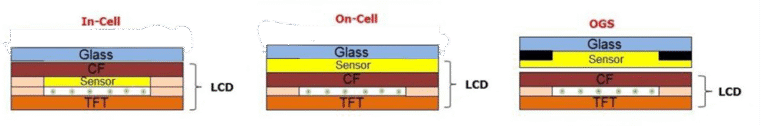
OLED displays consist of multiple thin layers of organic material sandwiched between electrodes. When voltage is applied, electrons and holes combine in the emissive layer, producing light.
The structure typically includes:
- Substrate layer: Provides mechanical support (often glass or flexible plastic).
- Anode layer: Removes electrons, creating “holes” that attract electrons.
- Organic layers:
- Conductive layer (transports holes).
- Emissive layer (produces light).
- Cathode layer: Injects electrons.
Because each pixel is its own light source, OLED panels do not require bulky backlighting systems, resulting in thinner and lighter displays.
Types of OLED Displays
There are several variations of OLED technology, each optimized for different use cases:
- PMOLED (Passive Matrix OLED):
Simple design, cost-effective, but limited in resolution and size. Suitable for wearables and small displays. - AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED):
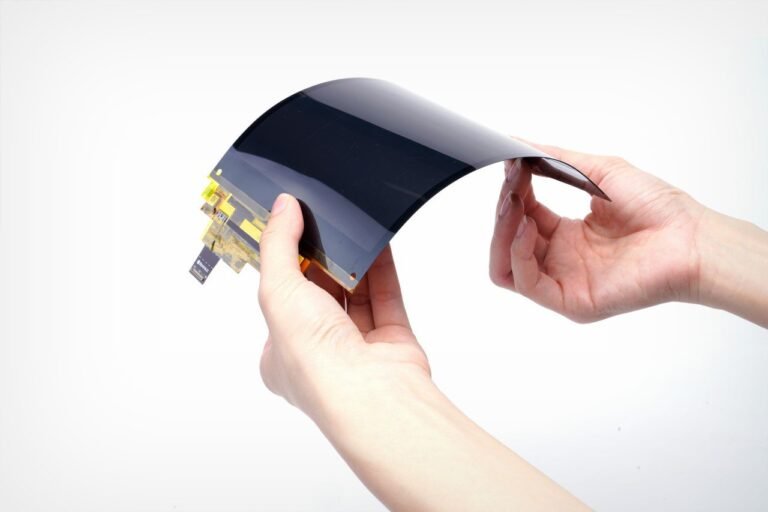
Uses thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control each pixel. This enables higher resolutions, faster refresh rates, and better efficiency. Widely used in smartphones, tablets, and TVs. - Flexible OLED:
Built on plastic substrates, enabling curved, foldable, and rollable displays. - Transparent OLED:
Allows light to pass through when not in use, opening possibilities in smart windows, automotive displays, and retail signage.
OLED vs LCD: The Core Differences
To understand why OLED is considered superior in many cases, let’s compare OLED vs LCD:
| Caraterística | OLED Display | LCD Display |
|---|---|---|
| Fonte de luz | Self-emissive (each pixel lights up) | Requires backlight |
| Níveis de preto | True black, infinite contrast | Greyish blacks due to backlight bleed |
| Ângulos de visualização | Wide, consistent colors | Narrower, color shifts at angles |
| Thickness | Ultra-thin, flexible options | Thicker due to backlight layers |
| Eficiência energética | More efficient for dark content | Consumes more power overall |
| Lifespan | Limited by organic material aging | Longer lifespan in static use cases |
Advantages of OLED Displays
- True Black and Infinite Contrast
Since pixels can be turned off completely, OLED achieves perfect blacks and stunning contrast ratios. - Superior Color Accuracy
OLED can reproduce a wide color gamut, making it ideal for HDR content. - Thinner and Lighter Designs
With no backlight required, OLED displays can be ultra-thin and even flexible. - Faster Response Times
OLEDs offer near-instant pixel response, reducing motion blur in gaming and video. - Flexible Applications
Enables foldable smartphones, curved TVs, and automotive HUDs.
Limitations of OLED Displays
- Burn-in Effect
Prolonged display of static images can cause ghosting or “burn-in.” - Shorter Lifespan of Blue Pixels
Blue organic materials degrade faster, potentially impacting long-term color accuracy. - Higher Cost
Manufacturing OLED panels is more expensive than LCDs, especially for large displays. - Brightness Limitations
While OLED excels in contrast, peak brightness is sometimes lower than high-end LCDs (like Mini-LED).
Applications of OLED Displays
OLED technology has found widespread use in industries where visual performance and design flexibility matter:
- Eletrónica de consumo: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions.
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches, fitness bands, AR/VR headsets.
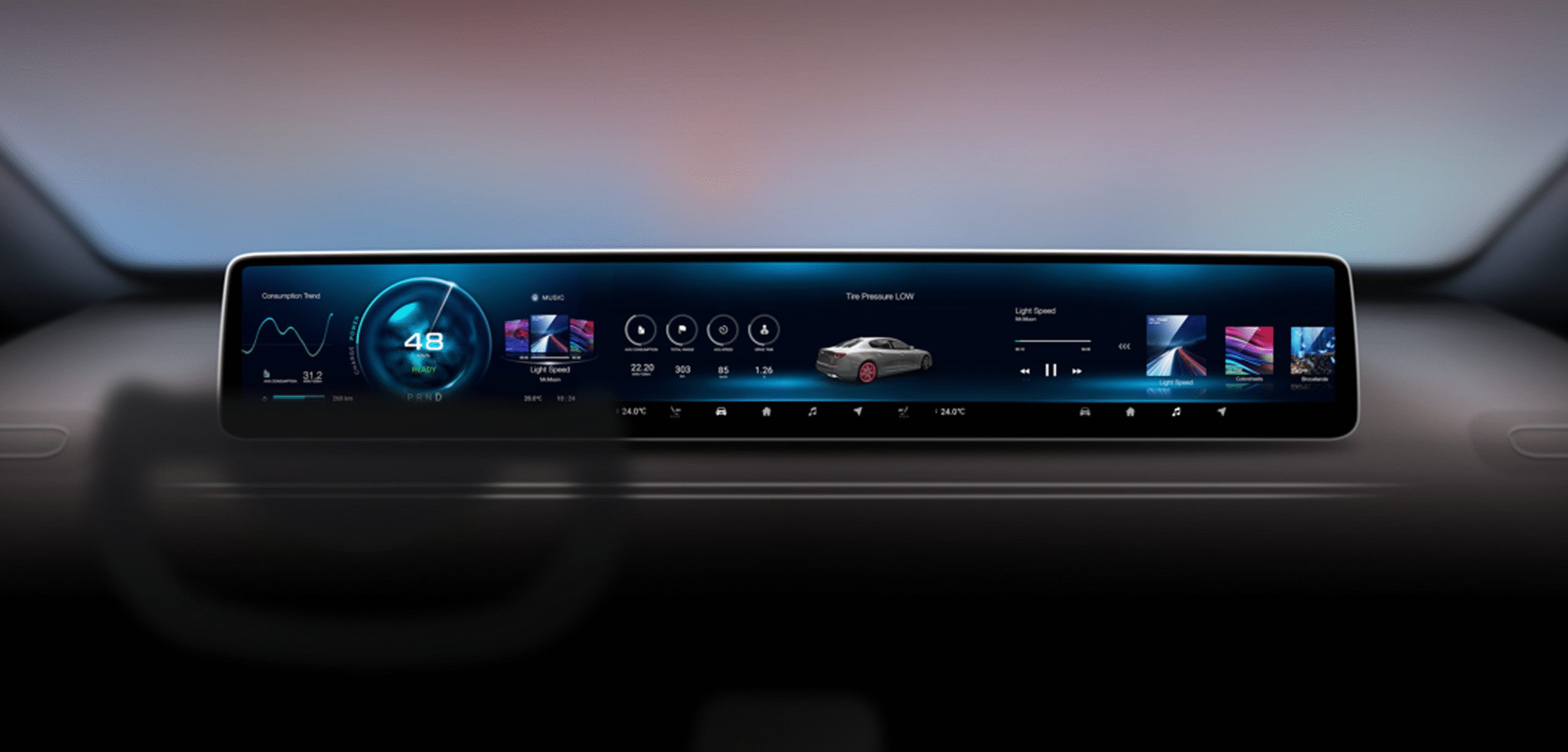
- Ecrãs para automóveis: Digital dashboards, infotainment systems, HUDs.
- Cuidados de saúde: Medical imaging and monitoring equipment.
- Retail and Advertising: Transparent OLED signage and flexible displays.
Why OLED Displays Are the Future
OLED is not just a trend—it represents a fundamental shift in display technology. With continuous improvements in manufacturing efficiency, material durability, and flexible design, OLED is expected to dominate high-end displays in the coming decade.
Emerging areas like roll-up TVs, foldable smartphones, and augmented reality glasses are only possible because of OLED’s flexibility and self-emissive nature.
Should You Choose an OLED Display?
The answer depends on your needs:
- If you prioritize image quality, color accuracy, and premium design, OLED is the best choice.
- If you want a cost-effective solution with long lifespan, LCD still has advantages.
For most modern consumer applications, OLED provides the ideal balance of aesthetics and performance.
Conclusão
So, what is OLED display? In essence, it is a self-emissive, organic-based display technology that delivers superior contrast, vibrant colors, and innovative form factors. Despite challenges like cost and burn-in, OLED continues to shape the future of screens across industries—from smartphones to smart cities.
With the growing demand for immersive experiences and sleek designs, OLED stands as a cornerstone technology that will redefine how we interact with digital content.