- 1 What is a Standard LCD Display?
- 2 What is a Round LCD Display?
- 3 Growing Market for Round LCD Displays
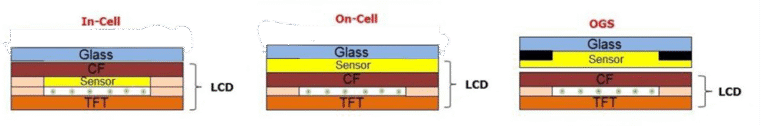
- 4 Technical Differences Between Round and Standard LCDs
- 5 Cost Structure of Standard LCD Displays
- 6 Cost Structure of Round LCD Displays
- 7 Engineering Requirements in Circular Display Manufacturing
- 8 Customization in Round LCD Modules
- 9 Interface Differences
- 10 Firmware and Driver Requirements
- 11 Volume and Yield Impact on Cost
- 12 Backlight Architecture for Round Displays
- 13 Comparison Table: Cost Drivers
- 14 Design and Aesthetic Advantages of Round LCD Displays
- 15 Long-Term ROI and Value of Round LCDs
- 16 Performance Comparison
- 17 FAQs
- 18 Conclusion
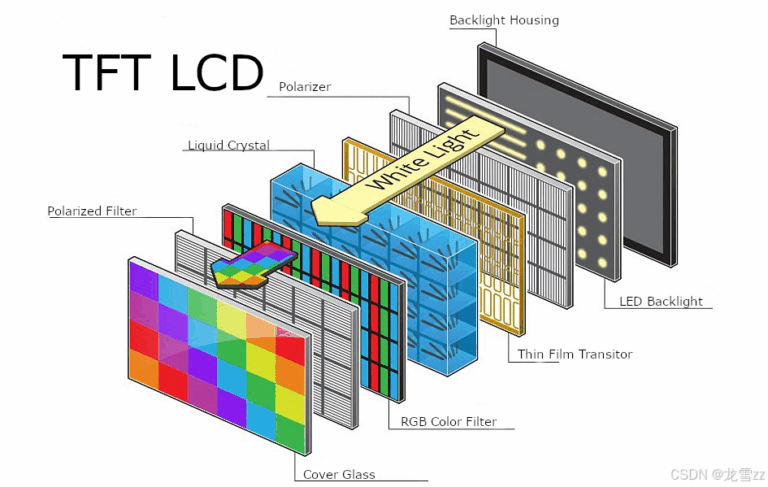
What is a Standard LCD Display?
Standard LCD displays refer to rectangular thin-film transistor (TFT) modules widely used in smartphones, tablets, monitors, POS systems, and embedded devices. They’re built on standardized manufacturing pipelines, where large glass substrates are sliced into rectangular segments for efficiency and scale.
- Aspect Ratios: 4:3, 16:9, or custom rectangular
- Mass-produced: Benefiting from supply chain economies
- Schnittstelle: Typically supports MIPI, RGB, LVDS, or HDMI
- Touch Support: Easily integrated with PCAP or resistive films
Due to their universality and modularity, standard LCDs are incredibly cost-effective for most use cases.

What is a Round LCD Display?
A round LCD display is a digital screen with a perfectly circular active area, designed specifically for space-limited or design-sensitive applications. Unlike rectangular screens, round displays are highly customized—requiring specialized processing to form their shape and ensure full pixel utilization within the circular bounds.
- Common Sizes: 1.28″, 2.1″, 3.4″, and up to 10.1″
- Anwendungsfälle: Smartwatches, vehicle dashboards, digital meters, rotary controls
- Struktur: Often integrates curved bezels, FPC connectors, and custom drivers
Despite having similar resolution or diagonal size as rectangular displays, round LCDs are usually twice as expensive due to their unique build.

Growing Market for Round LCD Displays
Die wearables revolution, combined with growing demand in smart home devices, automotive interfacesund medical wrist monitors, has created a strong market for round displays. Their aesthetic and ergonomic form gives brands a design edge in saturated consumer markets.
Trends Supporting Circular Displays:
- Smartwatches replacing analog dials
- Smart thermostats and kitchen controls
- Infotainment rings in automotive clusters
- Dial-style fitness and medical monitors
Technical Differences Between Round and Standard LCDs
Circular LCDs are not just rectangular LCDs trimmed into a circle. They involve:
- Custom TFT mask design for circular pixel layout
- Non-uniform backlight diffusion requiring radial LED arrangements
- Glass substrate optimization, where most of the rectangular panel is wasted
- Specialized ICs supporting non-linear coordinate mapping
This adds complexity across all stages—from fabrication to integration.
Cost Structure of Standard LCD Displays
| Komponente | Notes |
|---|---|
| TFT Glass | Cut efficiently from full panels |
| Touch Film | Standard PCAP sizes available |
| Backlight-Einheit | Straight-edge LED strips or light guides |
| IC & Controller | Mass-produced drivers |
| FPC | Pre-designed, standard trace routing |
| Assembly Yield | High, with minimal waste |
| Supply Volume | Very high—millions per batch |
Result: Low unit cost, easy integration, fast time-to-market
👉 Verwandte Lektüre: Aufbau und Funktionsweise von TFT-Flüssigkristallanzeigen
Cost Structure of Round LCD Displays
| Komponente | Notes |
|---|---|
| TFT Glass | Cut using laser or custom masks, more waste |
| Berührungsbildschirm | Curved ITO patterns, custom bonding |
| Backlight-Einheit | Radial LED layout, custom guides |
| IC & Controller | May require software calibration |
| FPC | Often bent or non-linear, special tooling |
| Assembly Yield | Lower, more defects at edge or seal areas |
| Supply Volume | Low-to-mid, custom orders only |
Result: 20%–100% higher cost per unit compared to rectangular displays
Engineering Requirements in Circular Display Manufacturing
Unlike rectangular LCDs, circular displays must address:
- Radial mechanical stresses
- Edge uniformity in pixel drive
- Symmetry in touch sensitivity
- Curved circuit routing and trace matching
All of this translates to longer production times, higher scrap rates, and more expensive test/validation cycles.
Customization in Round LCD Modules
Customization is almost always needed in:
- Touch Sensor Design: Either fully circular or ring-shaped PCAPs
- Cover Lens or Bezel: Must match circular viewing window
- Mechanical Mounting Points: Often asymmetric or embedded
- FPC Connector Placement: Offset or curved to fit round contours
These adjustments increase BOM and tooling costs.
Interface Differences
Circular LCD modules often rely on:
- SPI for low-speed control (IoT, wearables)
- MIPI-DSI for high-speed video (Android systems)
- Custom I²C bridges for touch controllers
Standard LCDs, by contrast, benefit from widespread, plug-and-play compatibility. Round displays may need custom drivers or kernel patches—especially in embedded Linux or Android environments.
Firmware and Driver Requirements
To fully utilize a round screen, you may need:
- Circular UI rendering libraries
- Coordinate remapping for touch
- Input mask filtering to avoid registering off-screen touches
Systems like Android, Qt, and LVGL require special configurations to support circular resolutions (e.g., 320×320, 360×360).
Volume and Yield Impact on Cost
Standard LCD panels are manufactured in volumes of tens of millions per year. Round displays? Often less than 100K units per model.
Lower yield and smaller batch runs increase:
- Per-unit labor cost
- Setup and calibration time
- Transportation and inventory holding risk
Backlight Architecture for Round Displays
Circular modules demand radial light uniformity, which involves:
- Circular light guide films (LGF)
- Arc-arranged LEDs
- Reflectors with concentric rings
Standard panels use straight bars or edge-light systems. As a result, round display backlighting is more expensive and harder to align for even brightness.
Comparison Table: Cost Drivers
| Factor | Standard LCD | Round LCD Display |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Utilization | 90%+ | ~60% |
| FPC Routing | Linear | Custom-curved |
| Touch Layer | Off-the-shelf | Custom pattern |
| Hintergrundbeleuchtung | Linear | Radial or concentric |
| Tooling Cost | Niedrig | Hoch |
| MOQ | 1K–5K | Often 500–1K |
| Driver Software | Generic | Custom/UI-specific |
Design and Aesthetic Advantages of Round LCD Displays
Now to the heart of your concern—why choose round despite higher cost?
- Iconic Visual Impact: Circular screens catch the eye and enhance product uniqueness
- Natural UX: Round shapes better match human interaction in wrist-wearables, knobs, and dials
- Focus-Centric Design: Users focus toward the center, ideal for real-time data and alerts
- Higher Perceived Value: Consumers associate round screens with innovation and luxury
- Improved Ergonomics: Especially in rotating UIs and gesture-controlled interfaces
Design isn’t an afterthought—it’s a strategic advantage, and round displays offer it in abundance.
Long-Term ROI and Value of Round LCDs
While round displays are costlier to produce, they:
- Enable higher pricing in consumer markets
- Differentiate brands in a crowded ecosystem
- Improve UX for critical applications (like medical or automotive)
- Offer future-forward design appeal that scales with software trends
For companies focused on design leadership or market disruption, round LCDs offer strong ROI beyond raw cost.
Performance Comparison
| Merkmal | Standard LCD | Round LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Helligkeit Gleichmäßigkeit | Hoch | Requires tuning |
| Touch Accuracy | Stable | Edge calibration needed |
| Stromverbrauch | Similar | Slightly higher (LED layout) |
| UI Optimization | Easy | Custom frameworks needed |
| Visual Appeal | Generic | Premium |
FAQs
Why do round LCDs cost more?
Due to lower yield, custom components, and higher design/tooling costs.
Can I use Android with a round display?
Yes, with proper drivers and UI adjustments (especially with LVGL or AOSP mods).
Sind runde Displays auch bei Sonnenlicht lesbar?
Some models offer 800–1000 nits brightness, suitable for outdoor applications.
What industries benefit most from circular displays?
Wearables, automotive clusters, medical diagnostics, and luxury home devices.
Can I get round LCDs with capacitive touch?
Absolutely—many models support multi-touch via custom PCAP.
Schlussfolgerung
Die cost difference between round LCD displays and standard LCDs is rooted in production complexity, customization, and lower volumes. But that cost brings substantial benefits in user experience, brand recognitionund design innovation. For products where interface, appeal, and usability define success—round displays are not an expense, but an investment.