The Dream Takes Shape: Early Concepts and Prototypes
Pioneering Proposals
The idea dates back to visionary inventors like Steve Mann, who sketched a bionic contact lens with an embedded display in 1999. These early ideas merged AR and miniature optics but remained conceptual due to technological constraints.
Google’s Smart Lens for Glucose Monitoring
In 2014, Google’s Verily unveiled a prototype sensory contact lens designed to measure glucose levels in tears with an embedded wireless chip and pinhole micro-sensor. Despite the innovation, the project was suspended in 2018, as tear glucose readings failed to correlate reliably with blood glucose.
Advanced R&D: CMST’s Electro-Optic Lens
Researchers led by De Smet in the 2010s developed thermoformed electro-optic layers inside a contact lens, including ultra-low power driver chips, micro-batteries, and hermetic protective coatings. This pioneering work demonstrated technical feasibility, albeit without full commercialization.
Breaking Ground: AR-Enabled Contact Lens Prototypes
Mojo Vision’s Ambitious Leap
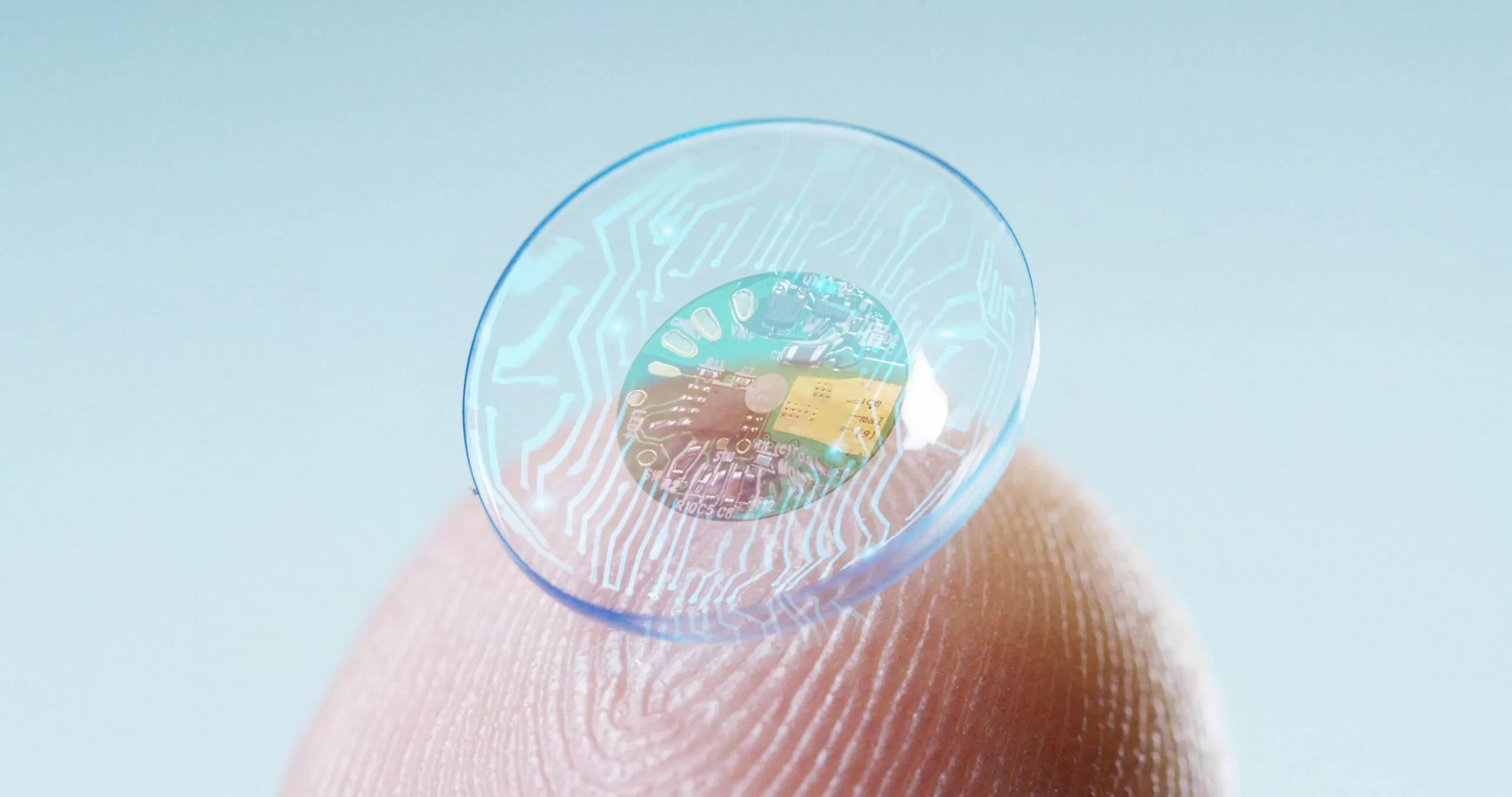
Mojo Vision, founded in 2015, delivered perhaps the most advanced prototype: a microLED display 와 함께 14,000 pixels per inch (PPI) just 0.5 mm in diameter, combined with motion sensors, eye tracking, a custom ASIC, and a wireless communication system. A CEO demo in 2022 showcased on-eye AR overlays such as compasses and teleprompters.
However, by 2023 Mojo Vision pivoted away from smart lenses and laid off 75% of staff, retaining only its microLED technology.
XPANCEO and Multi-Functional Lenses
More recently, XPANCEO (2025) secured $250 million funding to develop smart contact lenses offering AR, night vision, optical zoom, tear-based biomarker sensors, intraocular pressure monitoring, and wireless power transfer. These lenses aim for medical niches before possible consumer rollout in the 2030s.
Other Academic and Prototype Advances
- South Korean researchers demonstrated a glucose-alert LED lens, with tear fluid sensors triggering visual cues.
- Retina-embedded displays using conductive thin films advanced low-tech prototypes.
- Military research prototypes explored AR overlay lenses for soldiers.
The Technological Tightrope: Engineering Challenges
Miniaturization and Fabrication
Integrating a display, sensors, power source, radio, and driver IC into a tiny biocompatible lens demands ultra-precise microfabrication—thermoforming liquid-crystal cells, encapsulating circuitry against tear fluid, and ensuring oxygen permeability.
Power and Energy Constraints
Mini-batteries or wireless power via NFC may power prototypes briefly; yet continuous power remains a challenge, complicated by heat and safety concerns.
Biocompatibility and Comfort
Long-term wear demands biocompatible materials that allow tear exchange. Overwear risks irritation, infection, or corneal damage.
Visual UX and Optical Design
Fitting meaningful AR content into a narrow ~50° field of view while avoiding optic fatigue requires collimated retinas, minimal interface clutter, gaze-based input, and dynamic brightness compensation.
Health, Safety & Privacy
Soft contact lens misuse can cause serious health issues. Electronic implants that continuously record visual data raise huge privacy and surveillance risks.
Regulatory Barriers
As medical devices, smart lenses need FDA approval—requiring extensive clinical trials and long-term safety data.
Market Viability & Business Models
High manufacturing cost, unclear consumer demand, and speculative revenue models make business scaling difficult. Mojo Vision’s pivot and Verily’s discontinued project illustrate these economic limits.
The Market Retreat: Why the Concept Lost Momentum
We’ve seen pioneering projects reach working prototypes—but none have reached market viability, for several intertwined reasons:
- Technical Overreach – multiple engineering hurdles remain unsolved.
- High Costs – manufacturing is too expensive.
- Funding Constraints – R&D investors pulled back.
- Regulatory Complexity – lengthy approvals deter momentum.
- Consumer Reluctance – hesitation about putting electronics on the eye.
- Privacy & Ethics – invisible surveillance concerns.
Lessons Learned: Why the Market Turned Away
- 실현 가능성 ≠ 수요. 프로토타입이 존재한다고 해서 주류 소비자들이 이를 받아들일 것이라는 의미는 아닙니다.
- 안전 제일. 인간의 눈은 매우 민감하므로, 안전한 대중화를 위해서는 거의 완벽한 생체 적합성이 요구됩니다.
- 더 나은 대안. AR 안경과 스마트폰이 여전히 더 실현 가능합니다.
- 집중된 응용 분야가 승리합니다. 안압 센서와 같은 의료용 렌즈가 더 빠르게 발전하고 있습니다.
앞으로의 길: 이 아이디어는 다시 돌아올까?
광범위하게 내장된 디스플레이 렌즈는 상업적으로 출시되지 못했지만, 지속적인 트렌드가 개념의 일부를 부활시킬 수도 있습니다:
- 의료 응용 분야 – XPANCEO의 생체 표지자 및 녹내장 모니터링 렌즈.
- 하이브리드 디자인 – 수동 AR 광학 장치가 있는 처방 렌즈.
- 눈을 사용하지 않는 웨어러블 – 실용적인 솔루션으로서의 AR 안경.
- 구성 요소 기술 – Mojo Vision의 microLED가 다른 기기에 혜택을 줍니다.
- 윤리적 프레임워크 – 미래 채택을 위해 필요한 규제와 신뢰.
결론
콘택트렌즈에 내장된 LCD 디스플레이의 여정은 미래를 향한 주목할 만한 기술적 꿈이었습니다. 이는 마이크로 전자 공학, 광학 및 인간-기계 인터페이스 분야의 혁신을 요구하는 꿈이었습니다.
Google, Mojo Vision, XPANCEO와 같은 선구자들이 놀라운 발전을 이루었지만, 기술적, 건강 관련, 경제적, 윤리적 장벽들로 인해 결국 주류 채택은 주변화되었습니다.
기술이 더욱 발전함에 따라, 특히 의료 및 보조 분야에서 하이브리드 또는 부분적인 구현이 여전히 성공할 수 있습니다. 하지만 현재로서는 내장형 디스플레이가 있는 스마트 콘택트렌즈는 여전히 미래의 비전일 뿐… 아직 현실이 되지는 못했습니다.