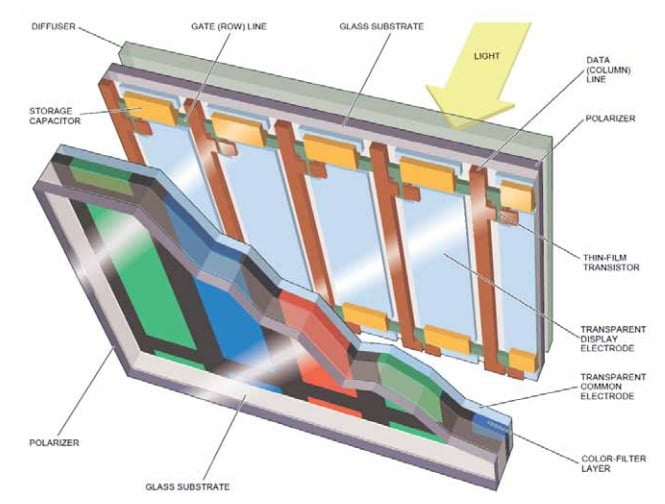
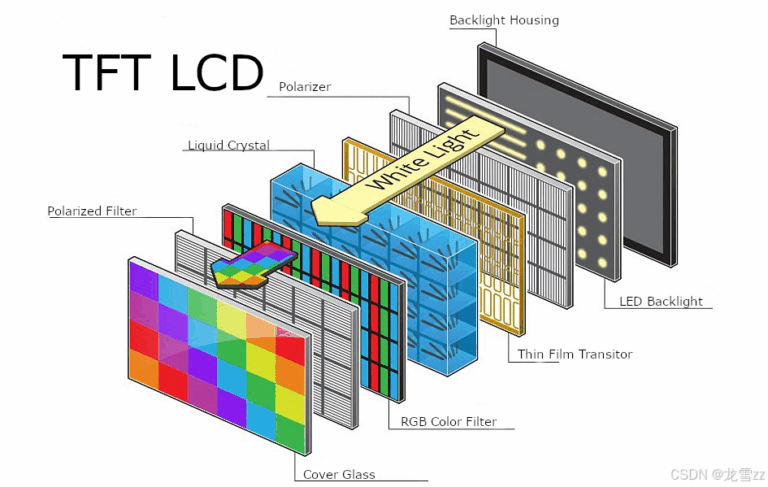
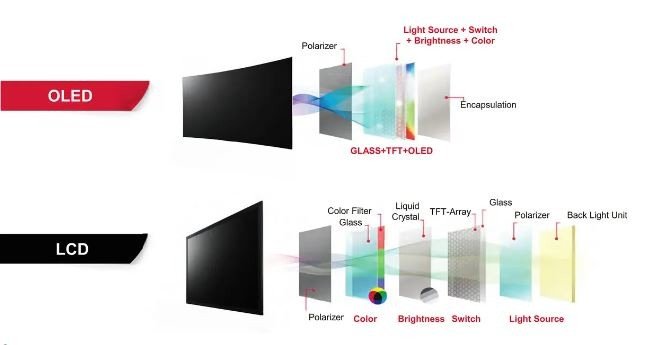
Fundamental Structure of TFT-LCDs
The intricate and precise structure of TFT-LCDs forms the foundation for their exceptional display capabilities. Key components include:
- 유리 기판: Serve as the primary structural base, housing the liquid crystal and transistor elements.
- Transparent Conductive Films: Typically made from indium tin oxide (ITO), these films function as electrodes, facilitating the application of electric fields to control pixel states.
- 액정 레이어: Situated between two glass substrates, this layer comprises liquid crystal molecules that align differently under electric fields, modulating light transmission.
- Color Filters: Positioned above the liquid crystal layer, these filters separate incoming light into red, green, and blue components, enabling full-color display.
- Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) Array: Each pixel is driven by a TFT, acting as a switch to regulate the voltage applied to the liquid crystal, thereby controlling light modulation.
Operational Principle of TFT-LCDs
TFT-LCDs operate based on the electro-optic properties of liquid crystals and the precise control provided by TFTs.
- Signal Transmission: Electrical signals are sent through transparent conductive films to the TFTs, which act as switches for individual pixels.
- Liquid Crystal Alignment: Activation of a TFT applies a voltage across the liquid crystal layer, causing molecules to align in a manner that modulates light transmission.
- Color Filtering: Light passing through the liquid crystal layer is filtered by color filters, producing red, green, and blue light components for each pixel.
- Image Formation: By controlling the voltage applied to each pixel, TFT-LCDs can display images with high clarity and color accuracy.
카탈로그에는 수천 개의 제품이 있습니다.
LCD-TFT, OLED 그래픽 및 영숫자 디스플레이, LCM, 전자 종이 디스플레이, 바코드 스캐너(내장형, 핸드헬드, 고정 마운트), 산업용 모니터, 산업용 컴퓨터(캐리어 보드, COM 및 SOM, 임베디드 시스템, HMI 패널 컴퓨터, SBC), 정전 용량 및 저항막 터치 스크린, 액세서리(개발 키트, 커넥터, 컨트롤러, FPC/FFC 테이프, ZIF 커넥터) 등 다양한 제품을 만나보세요.
Design Considerations for TFT-LCD Driver Systems
The design of driver systems is crucial for the performance of TFT-LCDs. Key considerations include:
- Signal Integrity: Ensuring high-quality transmission of digital signals to prevent degradation of image quality.
- Timing Precision: Accurate generation of timing signals is essential to synchronize pixel activation and prevent display artifacts.
- 전력 소비량: Optimizing power usage is vital, especially for battery-powered devices, to extend operational life.
- Thermal Management: Managing heat generation is important to maintain display performance and longevity.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Designing to minimize electromagnetic interference ensures compliance with regulatory standards and prevents disruption to other electronic devices.
- Reliability and Lifespan: Utilizing high-quality components and rigorous testing protocols helps ensure the display’s durability under various operating conditions.
- Cost Optimization: Balancing performance requirements with manufacturing costs is essential for market competitiveness.
결론
The design and operation of TFT-LCDs are complex and multifaceted, involving a deep integration of materials science, electrical engineering, and optical physics. By understanding the structural components, operational mechanisms, and design considerations, manufacturers can develop displays that meet the evolving needs of consumers and industries alike. Ongoing research and innovation in this field promise to further enhance display technologies, offering richer visual experiences and broader applications in the future.