1. TFT-LCD Array Manufacturing: Laying the Foundation
The array manufacturing process is the first and one of the most crucial stages in the TFT-LCD production. It involves creating the thin-film transistor array that controls the liquid crystal display. This step consists of several sub-processes, including deposition, etching, and patterning.
Key Steps in Array Manufacturing:
- Glass Substrate Cleaning: The process begins with cleaning the glass substrates, which will eventually form the basis of the display panel. Any impurities or residues left on the surface of the glass can lead to display defects.
- Deposition of Thin Films: A thin layer of silicon (typically amorphous silicon) is deposited onto the glass substrate. This layer forms the base of the TFTs. Following that, conductive layers like indium tin oxide (ITO) are applied, which serve as electrodes for controlling the liquid crystal.
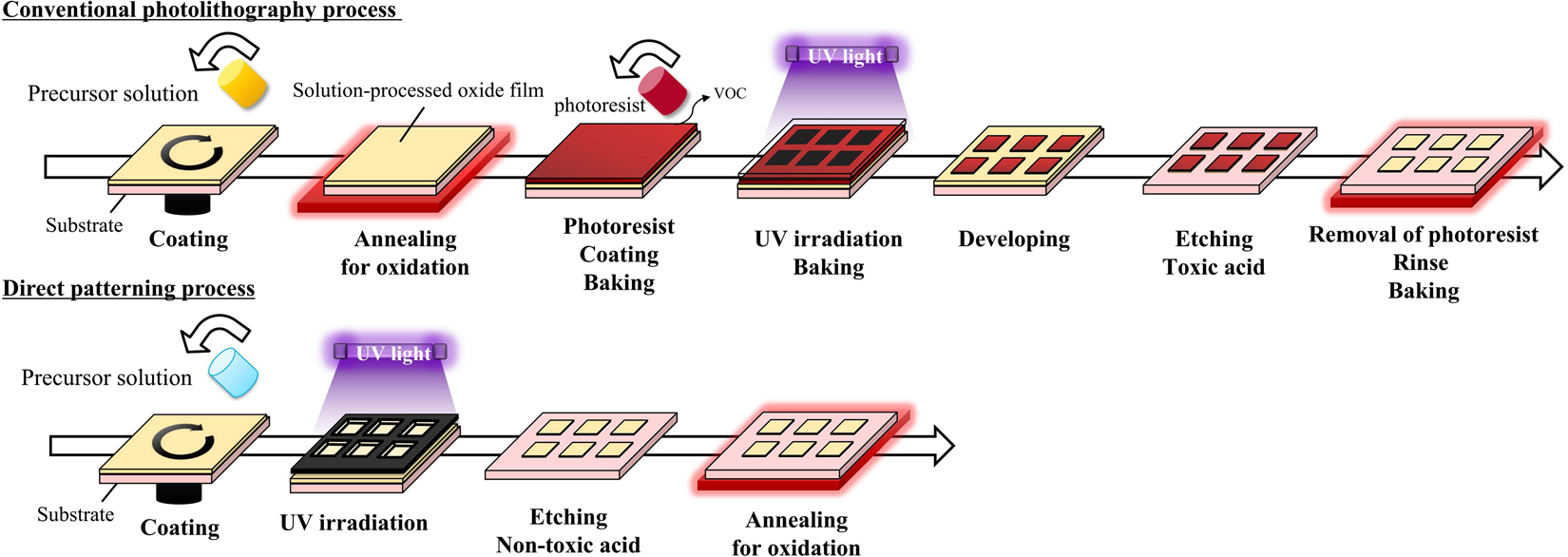
- Photolithography: A photolithography process is then used to define the pattern of the TFTs on the substrate. Using light and masks, precise patterns are transferred onto the substrate to create the array of TFTs. This step ensures the necessary control points for each pixel of the LCD.
- Etching: Once the pattern is transferred, the substrate undergoes etching to remove excess material and leave behind only the desired features of the TFT array.
2. Cell Manufacturing: Creating the Liquid Crystal Cells
After the array is manufactured, the next step in the TFT-LCD production process is creating the individual liquid crystal cells. This step involves the assembly of the liquid crystal layer between two glass substrates, with a layer of polarizing films on both sides.
Key Steps in Cell Manufacturing:
- Glass Lamination: Two glass substrates, one with the TFT array and the other with the color filter array, are laminated together. The two substrates are precisely aligned to ensure proper pixel placement.
- Liquid Crystal Injection: Once the substrates are laminated, liquid crystal material is injected into the gap between the two glass layers. This is a critical step, as the quality and type of liquid crystal material used directly affect the display’s visual performance.
- Sealing: The edges of the glass substrates are sealed to prevent leakage of the liquid crystal material. The sealing process also helps maintain the required alignment between the two glass layers.
- Alignment Layer: An alignment layer is applied to the inner surfaces of the glass to ensure that the liquid crystal molecules are oriented in the correct direction for optimal light modulation.
Des milliers de produits sont disponibles dans notre catalogue.
Découvrez notre large gamme de produits, notamment les écrans LCD-TFT, les écrans graphiques et alphanumériques OLED, les LCM, les écrans e-paper, les lecteurs de codes-barres (embarqués, portables, fixes), les moniteurs industriels, les ordinateurs industriels (cartes porteuses, COM et SOM, systèmes embarqués, ordinateurs à panneau HMI, SBC), les écrans tactiles capacitifs et résistifs, et les accessoires (kits de développement, connecteurs, contrôleurs, rubans FPC/FFC, connecteurs ZIF).
3. Module Manufacturing: The Final Assembly
The final step in the TFT-LCD manufacturing process is module assembly. This stage involves attaching additional components such as the backlight unit, touch panels, and the protective glass layer, forming the complete display module.
Key Steps in Module Manufacturing:
- Backlight Assembly: The backlight unit, typically consisting of LEDs, is attached to the display cell. The LEDs provide the necessary illumination for the display, making it visible under various lighting conditions. The backlight is usually combined with a light guide plate (LGP) to evenly distribute light across the screen.
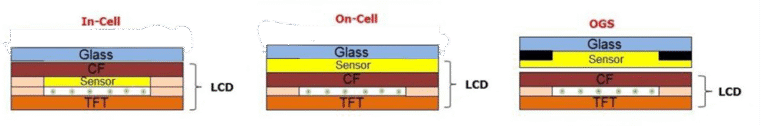
- Touch Panel Integration: In many modern TFT-LCDs, a touch panel is integrated into the display module. Capacitive or resistive touch panels are applied depending on the device’s requirements.
- Traitement de surface: To ensure optimal image quality, the surface of the LCD panel is often treated with anti-glare, anti-fingerprint, or anti-reflective coatings. These treatments improve usability and extend the lifespan of the display.
- Module Sealing and Testing: The final step in module manufacturing involves sealing the entire assembly to protect the internal components. The display is then tested for uniformity, brightness, and color accuracy. If any defects are found, the module undergoes further inspection or rework.
Conclusion
The TFT-LCD manufacturing process is a highly specialized and delicate procedure that involves multiple critical steps. From array creation to cell fabrication and module assembly, each phase plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets the high standards expected in modern display technology. As the demand for advanced displays continues to grow across various industries, innovations in manufacturing processes will likely continue to enhance the quality and efficiency of TFT-LCD production.