- 1 1. TFT and LCD: What’s the Relationship?
- 2 2. Why “TFT vs. LCD” is a Misleading Question
- 3 3. Types of LCD Technologies
- 4 Passive Matrix LCD (PM-LCD)
- 5 Active Matrix LCD (AM-LCD)
- 6 In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD
- 7 Super Twisted Nematic (STN) LCD
- 8 4. Advantages of TFT LCD Technology
- 9 ✅ Fast Response Times
- 10 ✅ Vivid Color Reproduction
- 11 ✅ High Resolution and Sharpness
- 12 ✅ Better Contrast Ratios
- 13 ✅ Wide Viewing Angles
- 14 5. Considerations When Choosing TFT LCDs
- 15 FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
1. TFT and LCD: What’s the Relationship?
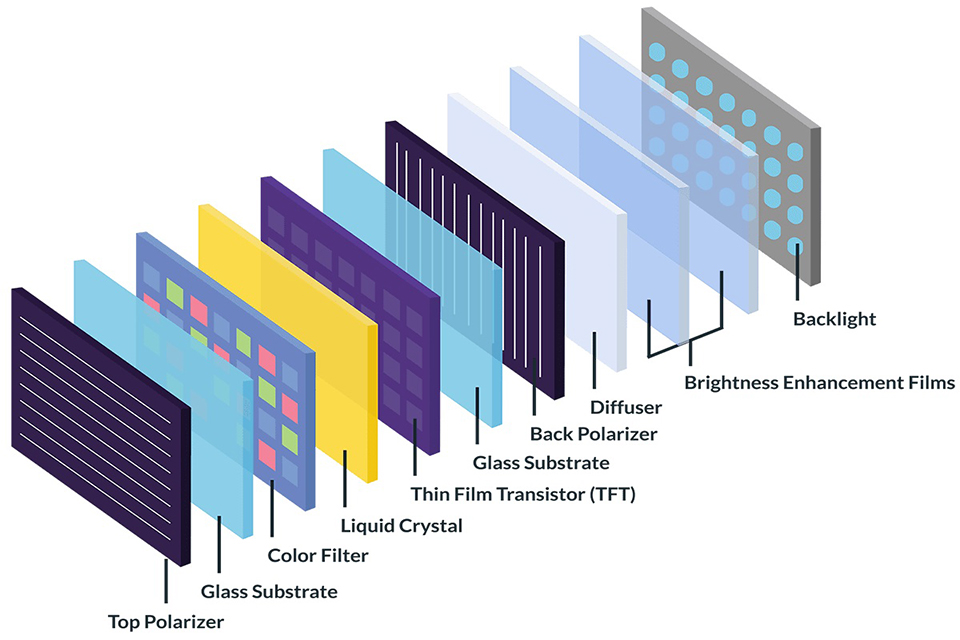
TLCD(液晶ディスプレイ) is a broad category of screen technology that uses liquid crystals and backlighting to produce images. These displays work by applying electrical signals to realign liquid crystal molecules, which then modulate light passing through them.
薄膜トランジスタ は specific type of active matrix LCD. It uses a thin-film transistor for each pixel, enabling precise control over image quality and response time. In short:
- All TFTs are LCDs
- Not all LCDs are TFTs
TFT describes how pixels are controlled—not whether the screen uses LCD technology (because it does).
In other words, TFT is a type of LCD, and all TFT displays are LCDs, but not all LCDs are TFT. The term “TFT” refers to the specific technology used to control the pixels within the LCD screen.
2. Why “TFT vs. LCD” is a Misleading Question
The term “TFT vs LCD” suggests these are two distinct technologies, when in fact TFT is a subset of LCD. A more accurate comparison would be TFT vs other types of LCD technologies, such as Passive Matrix or IPS.
The confusion often comes from how displays are marketed—some brands label basic LCDs as “LCD” and advanced versions as “TFT,” even though both use liquid crystal technology.
3. Types of LCD Technologies
LCD panels are built using different control methods. Here are the main types:
Passive Matrix LCD (PM-LCD)
This early LCD type uses a grid of horizontal and vertical lines to control pixels. It has slow response times, poor color depth, and low contrast. It’s now largely obsolete for modern applications.
Active Matrix LCD (AM-LCD)
Each pixel in an AM-LCD has its own transistor. This allows for fast refresh rates and better color control. 薄膜トランジスタ is the most popular active matrix type.
In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD
IPS is a type of active matrix LCD that improves color consistency and viewing angles by changing how the liquid crystals move. IPS displays still use TFT technology, but with a different alignment method inside the panel.
Super Twisted Nematic (STN) LCD
STN displays are improved passive matrix screens that offer better contrast and color than early PM-LCDs. However, they are slower than TFT and not suitable for fast-motion content.
4. Advantages of TFT LCD Technology
TFT has become the dominant LCD display type in consumer electronics, medical devices, industrial systems, and more. Here’s why:
✅ 迅速な対応
TFT controls each pixel individually, allowing fast image transitions. This reduces motion blur in videos and games.
✅ Vivid Color Reproduction
TFT displays show a wider color range with higher accuracy than passive matrix alternatives.
✅ High Resolution and Sharpness
The precise pixel control enables sharper images and crisp text, especially on small screens.
✅ Better Contrast Ratios
TFT technology provides deeper blacks and brighter whites, improving image depth and legibility.
✅ 広い視野角
While IPS offers the best angles, standard TFT displays still outperform older LCD types in this regard.
5. Considerations When Choosing TFT LCDs
Despite their strengths, TFT displays aren’t ideal in every situation. Keep these factors in mind:
Color-Critical Applications: If perfect color accuracy is essential, IPS (a TFT variant) may be a better choice due to its improved viewing angles and stable color output.
コスト: TFT is more expensive to produce than passive matrix displays. If you’re designing a budget device, PM-LCD or STN might be more appropriate.
電力使用量: TFT panels generally use more power. For battery-sensitive applications, choose low-power TFT variants or optimize display usage.
FAQ - よくある質問
Q1: What’s the difference between TFT and LCD?
A: TFT is a type of LCD—specifically, an active matrix LCD. TFT improves performance by giving each pixel a dedicated transistor for faster response and better color control.
Q2: Is IPS better than TFT?
A: IPS is a type of TFT LCD. It offers improved viewing angles and color accuracy but may have slower response times compared to standard TFT. It depends on your application needs.
Q3: Why are TFT displays more expensive?
A: TFT displays involve more complex manufacturing processes due to the thin-film transistors. They offer superior performance, which justifies the higher cost in many use cases.
Q4: Are TFT screens good for outdoor use?
A: They can be, especially if paired with high brightness and anti-glare coatings. However, transflective or reflective LCDs (often passive matrix) may be more readable in direct sunlight.
Q5: Can I use a TFT LCD in low-power devices?
A: Yes, but it may require optimization. Low-power TFT modules are available, and techniques like dimming backlight or reducing refresh rate can help.