- 1 What Are Android Displays?
- 2 Key Technologies Behind Android Displays
- 3 Display Panel Types
- 4 Touchscreen Technologies
- 5 Processing Units
- 6 Core Specifications to Consider
- 7 Advantages of Android Displays
- 8 Android Displays vs. Traditional Embedded Displays
- 9 Applications of Android Displays
- 10 Consumer Electronics
- 11 Automotive Industry
- 12 Industrial Automation
- 13 Retail & Hospitality
- 14 Education & Healthcare
- 15 Challenges and Limitations
- 16 Future Trends in Android Displays
- 17 Conclusion
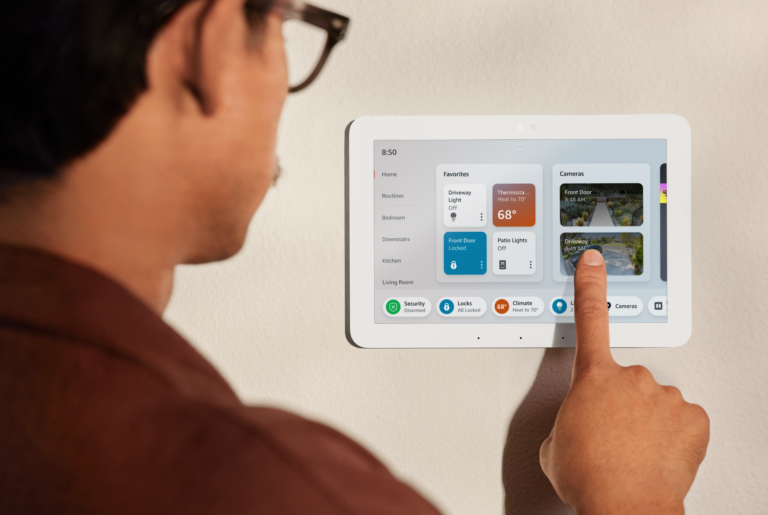
What Are Android Displays?
An Android display is a touchscreen-enabled display module powered by the Android operating system. Unlike traditional displays, which often require custom firmware or external processors to run applications, Android displays integrate:
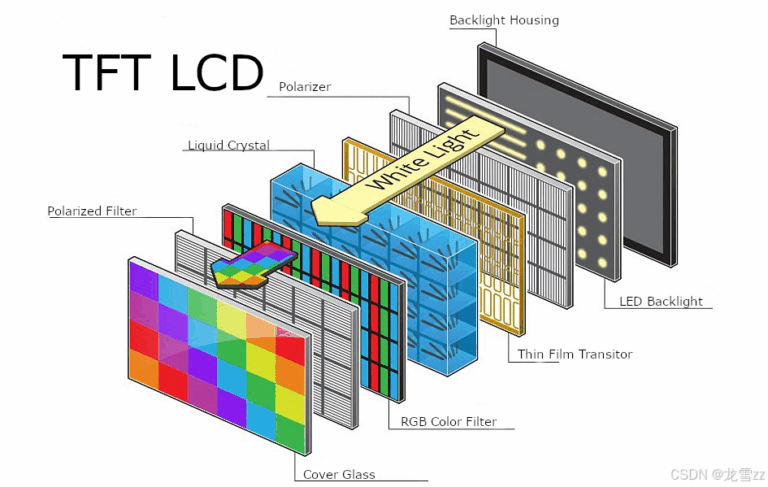
- Display panel (LCD, TFT, or OLED)
- Touchscreen layer (capacitive or resistive)
- Embedded computing hardware (CPU, GPU, memory, storage)
- Android OS as the software platform
This all-in-one structure makes Android displays self-sufficient computing devices, capable of running apps, managing connectivity, and supporting advanced user interfaces without additional controllers.
Key Technologies Behind Android Displays
The performance of an Android display depends on both display hardware 그리고 system-on-chip integration.
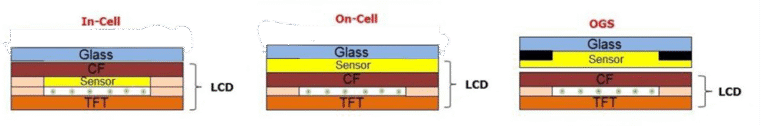
Display Panel Types
- LCD / TFT: Common for cost-effective and high-resolution requirements.
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): Delivers wider viewing angles and better color consistency.
- OLED: Offers vivid colors, deep blacks, and thinner form factors.
Touchscreen Technologies
- Capacitive Touch: Standard for smartphones, responsive and supports multi-touch.
- Resistive Touch: Still used in industrial settings where gloves or styluses are common.
Processing Units
Android displays are typically powered by ARM-based processors (Cortex-A series), integrating CPU + GPU for multimedia-rich applications.
Core Specifications to Consider
When selecting an Android display, engineers and integrators evaluate key specifications such as:
- Screen Size: Ranges from compact 4-inch panels to large 21-inch+ screens.
- 해상도: Standard HD (720p), Full HD (1080p), and increasingly 2K or 4K for high-end applications.
- 밝기: Indoor models often provide 300–500 nits, while outdoor units may exceed 1000 nits.
- Touch Response: Multi-touch capabilities (5-point or 10-point touch).
- Connectivity: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, and sometimes 4G/5G for mobile use.
- Interfaces: HDMI, USB, UART, and GPIO options for peripheral integration.
- Operating System Version: Android 9, 10, 11, or customized builds depending on hardware.
Advantages of Android Displays
The popularity of Android-powered displays stems from their unique advantages:
- Familiar User Interface – Users worldwide are accustomed to Android’s intuitive UI.
- Wide App Ecosystem – Support for millions of apps from the Google Play ecosystem or custom APKs.
- Customizability – Manufacturers can tailor the OS for industrial or automotive requirements.
- All-in-One Integration – Combines computing, connectivity, and touch interface in one module.
- Scalability – Suitable for small handheld devices and large signage displays.
- 비용 효율성 – Open-source Android platform reduces software development expenses.
Android Displays vs. Traditional Embedded Displays
| 기능 | Android Display | Traditional Embedded Display |
|---|---|---|
| OS Support | Android (full OS with apps) | Often no OS or custom firmware |
| User Interface | Touchscreen, advanced UI | Limited, basic menus |
| App Ecosystem | Millions of apps | Custom development required |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, 4G | Limited, often wired only |
| Use Case | Consumer + industrial | Mostly industrial |
This comparison highlights why Android displays are increasingly chosen in smart terminals and human-machine interface (HMI) projects.
Applications of Android Displays
소비자 가전
Smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs are the most common Android display devices, providing seamless multimedia experiences.
자동차 산업
Android-based infotainment and navigation systems dominate car dashboards, rear-seat entertainment, and digital instrument clusters.
산업 자동화
Factory equipment, medical monitors, and industrial HMI panels use Android displays for data visualization and operator interfaces.
Retail & Hospitality
Interactive kiosks, point-of-sale (POS) terminals, and digital signage often rely on Android displays for customer engagement and smooth operation.
Education & Healthcare
Tablets and display panels in classrooms and hospitals use Android OS for remote learning, patient monitoring, and digital records.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, Android displays face some challenges:
- Fragmentation: Different versions and hardware platforms can complicate app compatibility.
- Security: Open-source systems may be vulnerable without regular updates.
- Longevity: Consumer-grade Android devices may not meet industrial-grade lifecycle requirements.
- 전력 소비량: High-performance displays with large screens consume more energy.
Future Trends in Android Displays
The Android display market continues to evolve with technological advancements:
- 5G Integration: Faster connectivity for IoT and cloud-based applications.
- Edge AI Processing: On-device AI for image recognition, voice commands, and predictive analytics.
- Flexible and Foldable Displays: Expanding from smartphones into embedded applications.
- Enhanced Security: Enterprise-grade Android builds with long-term update support.
- Smart City Integration: Android-based kiosks and signage as part of intelligent infrastructure.
Market analysts predict steady growth, with Android display shipments increasing in automotive, industrial, and retail sectors through 2030.
결론
Android displays represent the convergence of display technology, embedded computing, and a globally familiar software ecosystem. They offer unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for a wide range of industries.
From everyday consumer devices to mission-critical industrial applications, Android-powered displays continue to redefine how humans interact with machines. As advancements in connectivity, AI, and display technology unfold, their role will only grow stronger.
For businesses and engineers, investing in Android displays means choosing a platform that balances innovation, usability, and long-term adaptability.