Define LCD Display: Basic Definition
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a non-emissive, light-modulating device that uses liquid crystals to control light transmission. These crystals do not generate light directly; instead, they manipulate light from an external source (typically an LED backlight) by controlling its polarization state under the influence of an electric field.
In summary, to define liquid crystal display, we refer to a display module where image formation is accomplished by altering the optical alignment of birefringent liquid crystal molecules.
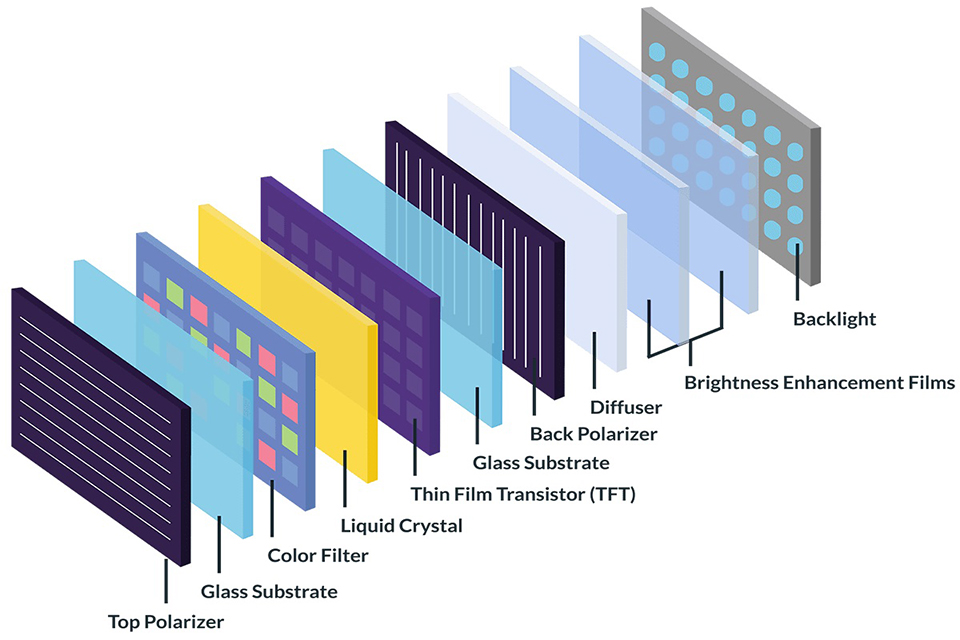
Layered Structure of an LCD Display
To fully define LCD display technology, we must examine its physical architecture. A typical TFT LCD module consists of the following layers (from bottom to top):
| Layer | Function |
|---|---|
| Backlight Unit | Provides illumination (edge-lit or direct-lit LEDs) |
| Bottom Polarizer | Converts unpolarized light to linear polarized light |
| TFT Glass Substrate | Hosts thin-film transistors and pixel electrodes |
| Liquid Crystal Layer | Changes molecular alignment to modulate light |
| Color Filter Substrate | Defines RGB subpixels for color rendering |
| Top Polarizer | Works with bottom polarizer to block/pass light |
| Cover Lens (Optional) | Provides protection or touch input interface |
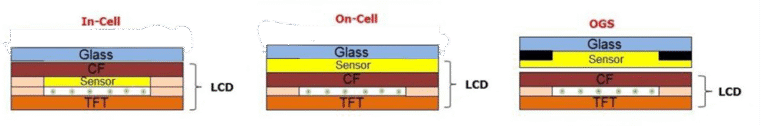
In capacitive touchscreen modules, a projected capacitive touch panel (PCAP) may be laminated on top using optical bonding or air gap lamination.
How Does an LCD Work? The Electro-Optical Principle
The fundamental concept in LCD operation is the control of light polarization by electrically driven liquid crystal molecules.
Key Operating Steps:
- Backlight emits white light, which enters the bottom polarizer.
- Liquid crystals are pre-aligned in a specific twisted configuration (e.g., 90° in TN mode).
- When no voltage is applied, the twisted molecules rotate the polarization of light, allowing it to pass through the top polarizer.
- When voltage is applied, the crystals align along the field, disrupting rotation and blocking light at the top polarizer.
- This binary light modulation creates contrast and grayscale levels via analog driving voltages.
In color displays, each pixel comprises three subpixels (RGB) with independent control to create full-spectrum color through additive mixing.
👉 Related reading: Structure and Driving Principle of TFT Liquid Crystal Display
Types of LCD Technology
When we define LCD display modules, it’s essential to distinguish the main alignment modes:
| Technology | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
| TN (Twisted Nematic) | 90° twist in crystals | Fast response, low cost, limited angle |
| IPS (In-Plane Switching) | Horizontal alignment | Wide angle, accurate color, slower response |
| VA (Vertical Alignment) | Vertical rest state | High contrast, moderate angle |
| Transmissive | Full backlight reliance | Indoor-focused, high brightness |
| Transflective | Partial ambient reflection | Outdoor-readable, moderate contrast |
Each alignment type impacts viewing angle, contrast ratio, response time, and cost structure.
👉 Related reading: A Comprehensive Comparison of LCD Panel Types: TN, VA and IPS
Thousands of products are available in our catalog.
Discover our wide range of products, including LCD-TFTs, OLED graphic and alphanumeric displays, LCMs, e-paper displays, barcode scanners (embedded, handheld, fixed mount), industrial monitors, industrial computers (carrier boards, COMs & SOMs, embedded systems, HMI panel computers, SBCs), capacitive and resistive touch screens, and accessories (development kits, connectors, controllers, FPC/FFC tapes, ZIF connectors).
Driving Method and Interface Technology
To define LCD display from a control system perspective, consider how pixel data and drive voltages are managed.
- Active Matrix (TFT): Each pixel is controlled by a dedicated thin-film transistor and storage capacitor, minimizing crosstalk and increasing resolution.
- Interface Types:
- RGB Parallel: For real-time direct drive with microcontrollers.
- SPI/QSPI: Low pin-count for compact systems.
- MIPI DSI: High-speed serial interface, common in smartphones.
- LVDS: Used in larger panels with high resolution.
Each interface choice affects bandwidth, latency, signal integrity, and layout complexity in embedded systems.
Performance Metrics That Define LCD Display Quality
| Metric | Technical Specification |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Number of pixels (e.g., 1280×960) |
| Pixel Pitch | Distance between centers of adjacent pixels |
| Brightness | Typically 250–1000 cd/m² |
| Contrast Ratio | Ratio of light/dark levels (e.g., 800:1) |
| Viewing Angle | Max angle without significant distortion |
| Response Time | Time to switch states (e.g., <20 ms) |
| Color Depth | Number of displayable colors (e.g., 16.7M) |
| Operating Temperature | Range suitable for stable function |
Define LCD Display in Embedded System Design
LCD modules are tightly integrated into embedded electronics and HMI systems. Considerations for integration include:
- Power Budget: LCDs with LED backlight require 3.3V–12V drivers.
- PCB Layout: High-speed interface signals (MIPI, RGB) need impedance control.
- EMI Shielding: Especially in capacitive touch modules.
- Firmware Compatibility: Display controllers must match resolution and timing.
Engineers typically rely on datasheets, EVBs (evaluation boards), and STN/TFT driver IC libraries when designing for industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a liquid crystal in physics?
A liquid crystal is a state of matter between liquid and solid. Its molecules can flow like a liquid but retain directional ordering like a crystal, enabling light manipulation.
What is a transmissive LCD display?
It is an LCD type that uses a backlight as its sole light source. Light passes entirely through the liquid crystal layers to generate images.
How is TFT different from LCD?
TFT (Thin Film Transistor) is a technology used to drive pixels in LCDs. All TFT displays are LCDs, but not all LCDs use TFT.
Is MIPI better than SPI for LCD?
MIPI offers higher bandwidth and better power efficiency but is more complex to implement. SPI is easier for low-speed applications.
Can LCDs be used outdoors?
Yes, if brightness exceeds 500 cd/m² and optical bonding or transflective layers are applied. UV-resistant coatings and anti-glare treatments also help.
🔧 Need Expert Guidance for Your LCD Project?
📧 Contact us at rjoytek@rjyi.net
🌐 Visit: https://rjydisplay.com/custom-solutions