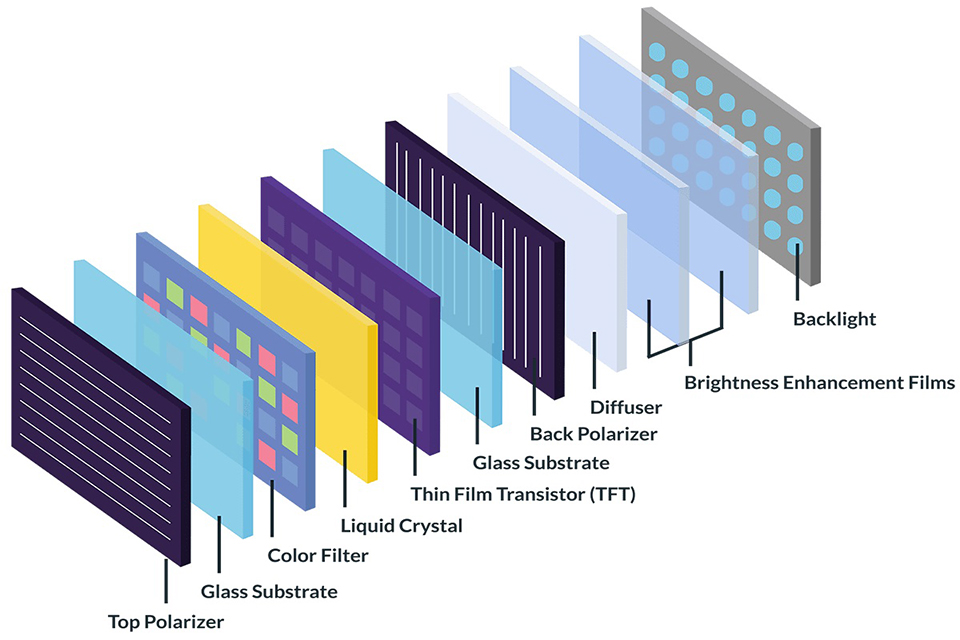
Polarizers: Directing the Light That Makes Images Visible
At the front and rear of every LCD lies a polarizer—a thin optical filter that controls the alignment of light waves.
The rear polarizer aligns backlight output.
The front polarizer filters the manipulated light after passing through the liquid crystals.
Without polarizers, you’d see no contrast or image—only a blank panel.
🧠 Tip: Polarizer quality directly affects viewing angles and ambient light readability.
Glass Substrates: Supporting Structure and Pixel Precision
Two glass layers sandwich the liquid crystal material, forming the structural foundation of the display.
These substrates house the TFT array and color filter while ensuring perfect pixel alignment.
They also serve as barriers against mechanical damage and environmental exposure, preserving image consistency and long-term durability.

Liquid Crystal Layer: The Core Light Valve of LCD Technology
This is the functional heart of every LCD. When voltage is applied, liquid crystals reorient to either block or transmit light.
This process controls:
- Brightness
- Contrast
- Gray levels
The precision of this modulation determines how smooth or pixelated the on-screen content looks.
🧪 Read more: Understanding LCD Display Pixel Term, Resolution & Aspect Ratio
Thousands of products are available in our catalog.
Discover our wide range of products, including LCD-TFTs, OLED graphic and alphanumeric displays, LCMs, e-paper displays, barcode scanners (embedded, handheld, fixed mount), industrial monitors, industrial computers (carrier boards, COMs & SOMs, embedded systems, HMI panel computers, SBCs), capacitive and resistive touch screens, and accessories (development kits, connectors, controllers, FPC/FFC tapes, ZIF connectors).
Color Filter: Converting Light Into Full-Spectrum Visuals
Each pixel is divided into three subpixels—Red, Green, and Blue (RGB)—by the color filter layer.
By varying voltage across the subpixels, LCDs mix millions of colors.
- Higher-grade filters enhance color saturation
- Uniform coating ensures consistent performance across the display
This is especially critical in medical imaging, digital signage, and professional graphic applications.
TFT Array: Controlling Each Pixel in Real Time
The Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) layer forms a precise grid—containing a dedicated transistor for each subpixel.
These tiny transistors switch on/off based on signals from the driver IC, giving the display:
- High refresh rates
- Low power draw
- Accurate pixel-level control
TFT arrays are essential in automotive displays, industrial HMIs, and portable devices where quick response and reliability are key.
Backlight Unit: Providing the Light Source Behind the Panel
LCDs don’t emit light on their own—they depend on a backlight, typically made of:
- White LEDs
- Light guide films
- Diffusers and reflectors
A good backlight ensures:
- Uniform brightness
- Color accuracy
- Outdoor readability

💡 RJY Display offers high-brightness LCDs (1000+ nits) ideal for sunlight-readable industrial monitors.
Driver IC: The Smart Control Center of Every LCD
Think of the driver IC as the bridge between your device and the display module. It converts image data into electrical signals that:
- Control voltage in the TFT grid
- Sync with touch and brightness control
- Optimize refresh rate, gamma curves, and power efficiency
Advanced ICs also support custom resolutions, adaptive brightness, and low-latency performance.
Touch Panel (Optional): Enabling Interaction with Intelligence
Modern LCDs often integrate touch-sensitive overlays. Two main types exist:
- Capacitive Touch (PCAP) – Multi-touch, high precision, sleek design
- Resistive Touch – Single-point, glove-compatible, rugged

🧪 Read more: A Comprehensive Comparison of LCD Panel Types: TN, VA and IPS
At RJY Display, we customize touch interfaces for industries like:
- Medical diagnostics
- Outdoor terminals
- Factory automation panels
How These LCD Components Work Together
The performance of any LCD module is defined by how well these parts integrate:
| Component | Primary Role |
|---|---|
| Polarizers | Direct and filter light for visibility |
| Glass Substrates | Provide structure and alignment |
| Liquid Crystal Layer | Modulate light transmission per pixel |
| Color Filter | Render full-spectrum color |
| TFT Array | Enable individual pixel control |
| Backlight Unit | Provide illumination across display |
| Driver IC | Manage signal conversion and power regulation |
| Touch Panel | Allow interactive input (optional) |
Whether you need ultra-bright, sunlight-readable screens or low-power monochrome modules, understanding each part of LCD gives you an edge in product development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the most important part of LCD structure?
A: All parts are interdependent, but the liquid crystal layer, TFT array, and backlight are foundational for image generation and quality.
Q2: Can I use LCDs without a touch panel?
A: Yes. Touch layers are optional. Many industrial modules are display-only, while others use integrated capacitive or resistive overlays.
Q3: How does backlight brightness affect display visibility?
A: Higher brightness improves readability in sunlight but may increase power consumption. We optimize backlight performance for your environment.
Q4: What’s the benefit of customizing LCD components?
A: Tailoring pixel layout, brightness, touch interface, and shape improves performance in specific-use cases like automotive, wearable, or industrial.
Q5: Are polarizers replaceable in LCD modules?
A: In most commercial designs, polarizers are built-in and not serviceable. Damage to them often requires full panel replacement.
Reference Resources